Figure 2.
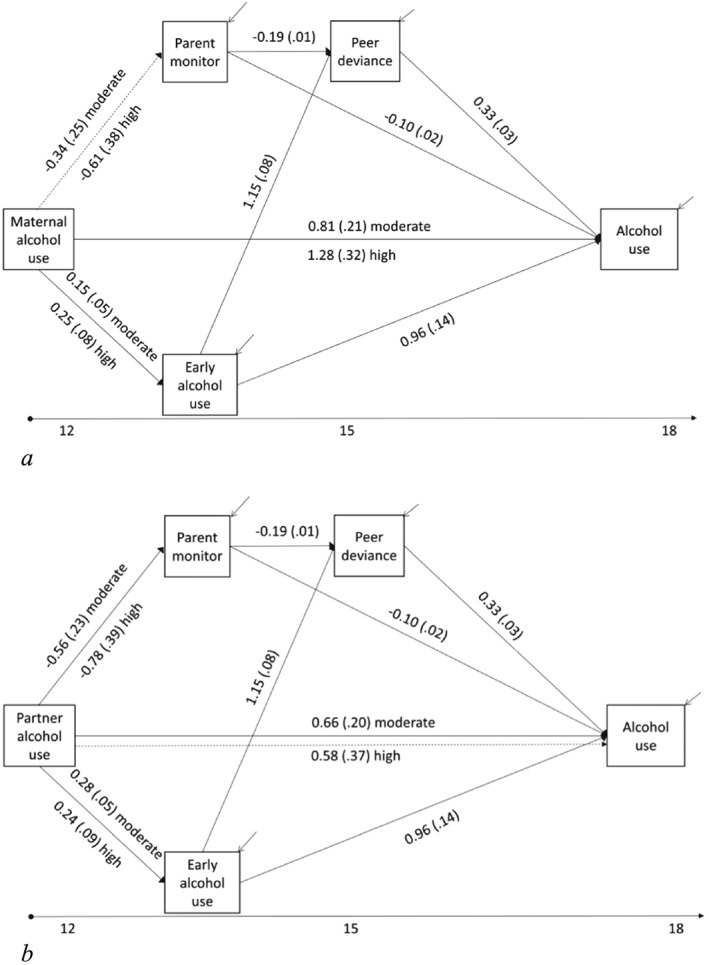
(a) Maternal alcohol use; (b) partner alcohol use. Path model showing the direct and indirect effects of parental alcohol use on young adult alcohol use through parental monitoring, peer deviance and alcohol use early in early adolescence, while adjusting for gender, maternal age at delivery, maternal smoking during pregnancy, family income, socio‐economic position, housing tenure and maternal education (inclusion of background covariates are not shown for ease of interpretation) (n = 3785). Dotted directional arrows indicate insufficient evidence of an association. Direct and indirect effects are obtained using the product of coefficients approach, whereby the indirect effects are derived by multiplying the parameters along each of the paths from exposure to outcome. For example, the indirect effect from partner moderate alcohol use to young adult alcohol use via early alcohol initiation and peer deviance is calculated by multiplying the coefficients along those paths (0.28 × 1.15 × 0.33 = 0.11)
