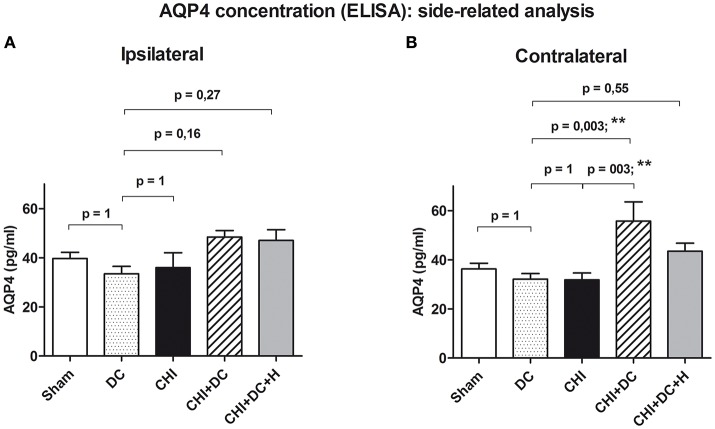
Figure 5.
Histogram presenting concentration of AQP4 24 h after trauma/sham injury according to ELISA assessment. This part of analysis involves the data pooled and averaged separately for the contralateral hemisphere (at the level of ROI plus outside the ROI) and for the ipsilateral one (again, at the level of ROI plus outside the ROI). (A) According to ANOVA, the differences between AQP4 level values, averaged for ipsilateral hemispheres were not significantly different between the treatment groups. (B) Analogous analysis in contralateral hemispheres revealed significant raise in AQP4 concentration in animals subjected to trauma and decompressive craniectomy as compared to non-traumatized reference group as well as to trauma-only group (CHI+DC vs. DC, p < 0.01, **; CHI+DC vs. CHI, p < 0.01, **). Similar to global pooled analysis, this effect could not be seen in group where hypothermia was added to the treatment (CHI+DC+H vs. DC, p > 0.05, ns). CHI, closed head injury; DC, decompressive craniectomy; H, hypothermia; ROI, region of interest.