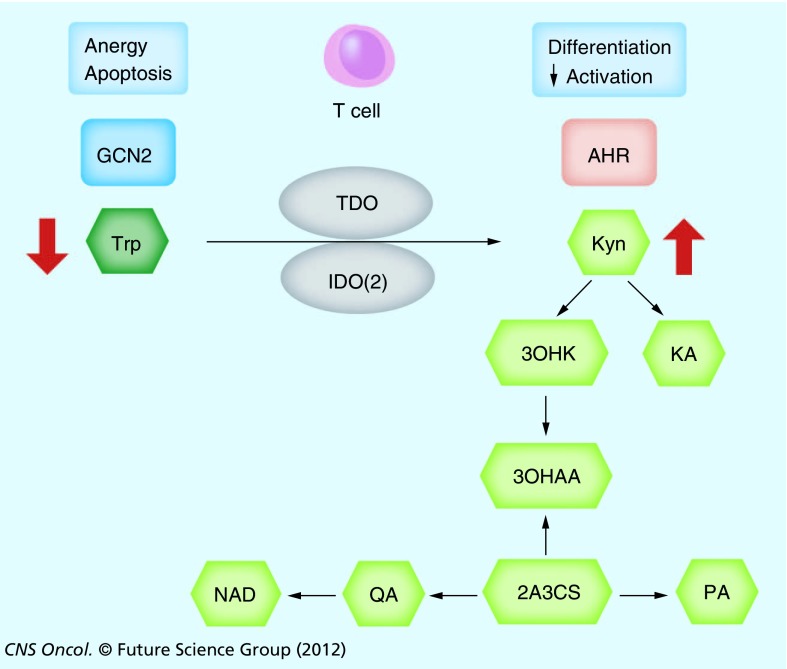
Figure 1. The kynurenine pathway.
Trp is metabolized in the local microenvironment by TDO or IDO or IDO2, resulting in a depletion of Trp and an accumulation of Kyn. Trp depletion leads to T-cell anergy and apoptosis by activating the GCN2 pathway. Kyn alters T-cell differentiation and suppresses activation by binding the aryl hydrocarbon receptor AHR. Kyn is further metabolized by enzymatic steps to KA, 3OHKA, 3OHAA, 2A3CS, PA and QA, which is ultimately processed to NAD.
2A3CS: 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate-semialdehyde; 3OHAA: 3-hydroxy-anthranilic acid; 3OHKA: 3-hydroxy-kynurenine; AHR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; GCN2: General control nonderepressable 2; IDO: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; KA: Kynurenic acid; Kyn: Kynurenine; PA: Picolonic acid; QA: Quinolinic acid; TDO: Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; Trp: Tryptophan.