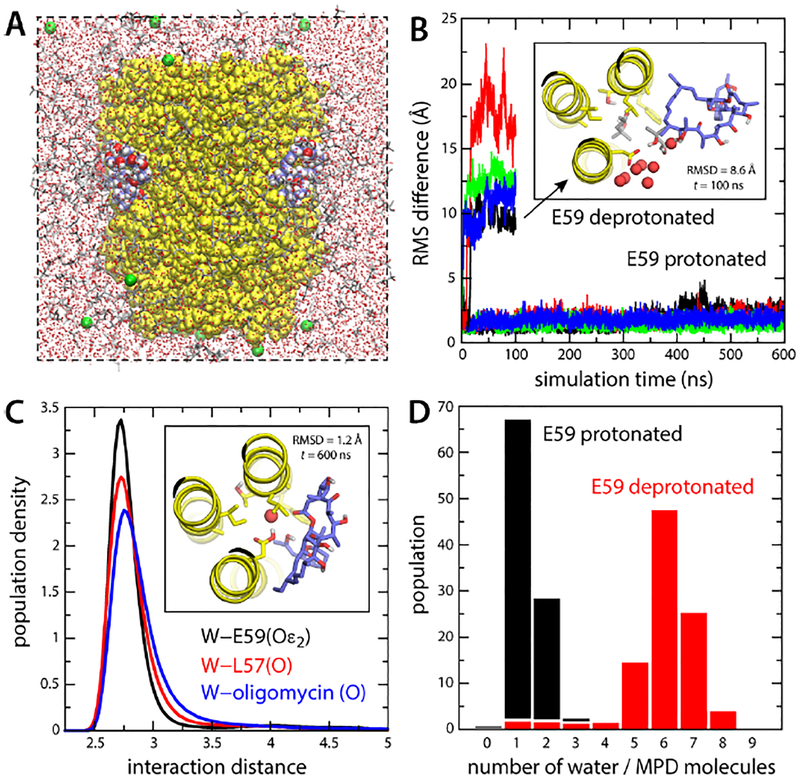
Figure 2. Simulations of the S. cerevisiae c10 ring with bound oligomycin, in an organic solvent.
(A) Simulation system comprising the c-ring (yellow) and four bound oligomycin molecules (blue/red/white spheres). The solvent is a mixture of MPD (red/grey sticks) and water (small red spheres). K+ ions (green spheres) neutralize the total charge. Hydrogen atoms in the solvent are omitted for clarity. (B) RMS deviation of each of the oligomycin molecules relative to the experimental binding pose (no hydrogens), as a function of simulation time, when Glu59 is protonated or deprotonated. The inset shows a snapshot of an oligomycin molecule partially dissociated when Glu59 is deprotonated, viewed from the matrix. Only 3 helices of the c-ring are shown for clarity (yellow). Residues lining the binding site, including Glu59, are highlighted (sticks). Neighboring water and MPD molecules are highlighted. (C) Persistence of the water-mediated network stabilizing oligomycin for protonated Glu59. The plot shows probability distributions, from a 600-ns trajectory, for the distance between this water molecule (oxygen atom) and the H-bond donors/acceptors in Glu59 (black), Leu57 (red) and oligomycin (blue). The inset shows one of the bound inhibitors at the end of the simulation. (D) Histogram of the number of water and MPD oxygen atoms coordinating Glu59, averaged over the four oligomycin sites, when Glu59 is protonated or deprotonated.