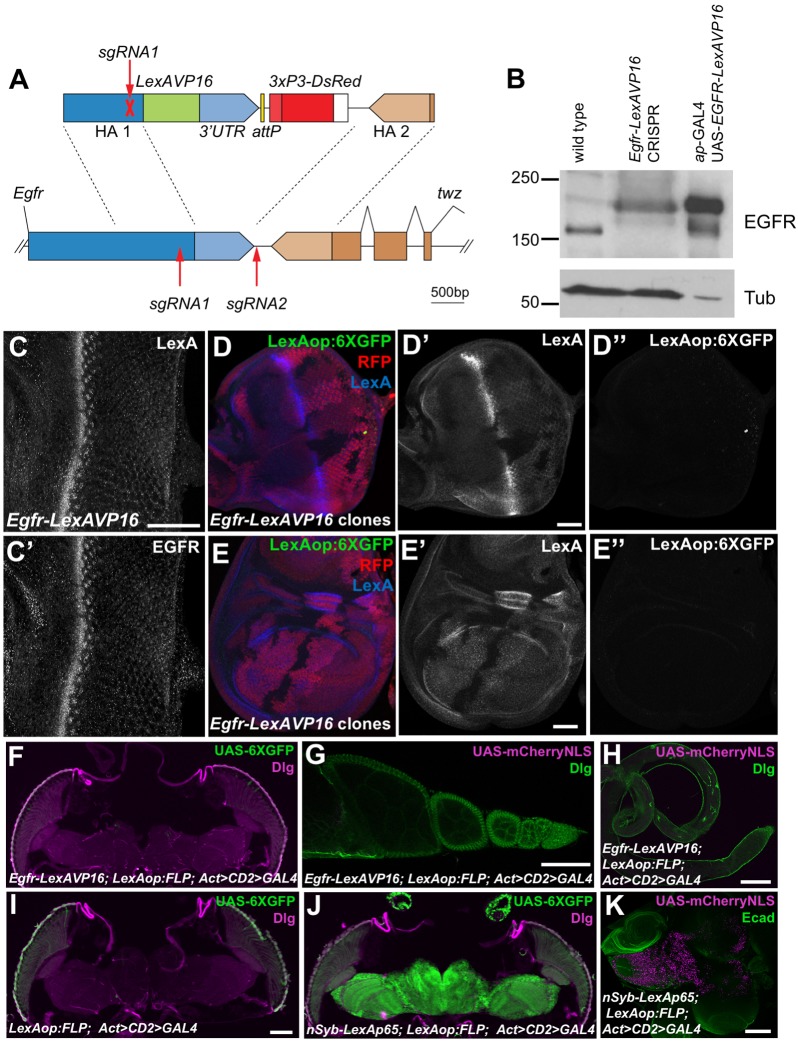
Fig. 3.
EGFR–LexAVP16 does not activate transcription when expressed at physiological levels. (A) The sgRNAs used to edit the endogenous Egfr sequence (lower) and the construct used for homology-directed repair (upper). (B) Western blot of lysates from wild-type and homozygous Egfr-LexAVP16 CRISPR adult flies and from ap-GAL4; UAS-EGFRLexAVP16 larval wing discs. In the CRISPR flies, EGFR is expressed at wild-type levels and migrates at the size for EGFR–LexAVP16. The wing disc extracts had much stronger EGFR–LexAVP16 expression and less protein was loaded. (C) Egfr-LexAVP16 eye disc stained with anti-LexA (C) and anti-EGFR (C′) antibody. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D,E) Eye disc (D) and wing disc (E) with clones lacking the Egfr-LexAVP16-modified locus marked by the absence of RFP (red) and LexA (D′,E′, blue). Anti-GFP antibody staining shows LexAop:6XGFP expression (D″,E″, green), which is not detectable in cells with Egfr-LexAVP16 above the background staining present in wild-type cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (F–H) Egfr-LexAVP16; LexAop:FLP; Act>CD2>GAL4 adult head (F), ovary (G) and testis (H) showing no expression of UAS-6×GFP stained with anti-GFP antibody (green, F) or of UAS-mCherry-NLS (magenta, G,H). (I) A negative control adult head without Egfr-LexAVP16. (J,K) nSyb-LexAp65; LexAop:FLP; Act>CD2>GAL4 induces strong expression of UAS-6×GFP in adult brain (J) and of UAS-mCherry-NLS in larval brain (K). F–J are stained for Discs large (Dlg, magenta in F,I,J; green in G,H) and K is stained for E-cadherin (Ecad, green). Scale bars: 100 μm.