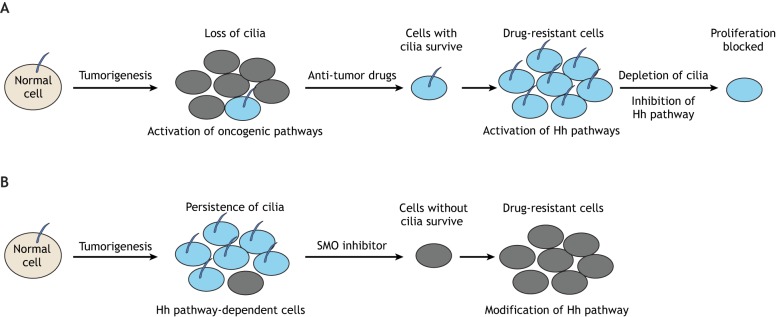
Fig. 5.
The function of primary cilia in cancer. (A) Loss of cilia has been observed in several types of tumors and can lead to aberrant activation of many oncogenic pathways. After treatment with anti-tumor drugs, tumor cells with cilia, and hence aberrant activation of Hh pathway, survive and can further proliferate. Depletion of cilia or inhibition of Hh signal pathway can block the proliferation of these drug-resistant cells. (B) The persistence of cilia can also be observed in a range of tumors, in which they appear to help maintain the oncogenic Hh pathway. After treatment with an SMO inhibitor, tumor cells with cilia die and the surviving cells (without cilia) evolve a modified Hh pathway that confers resistance to SMO inhibition.