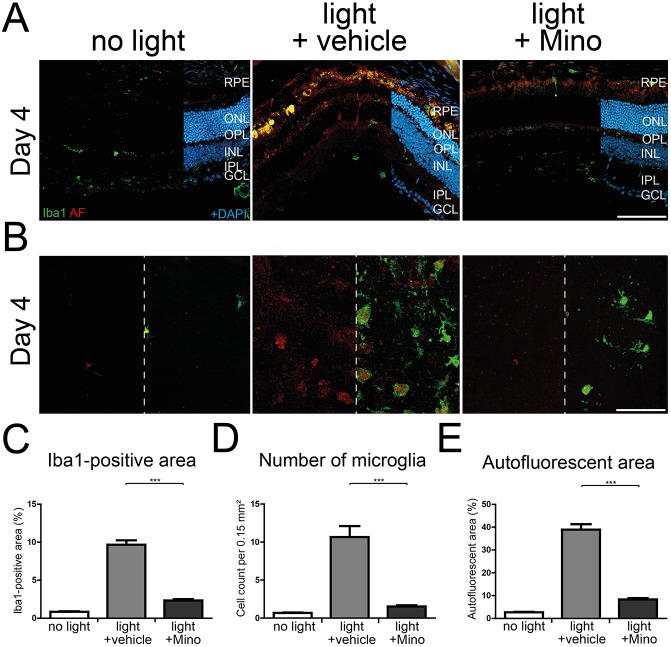
Fig. 8.
Lower microglial activity in minocycline-treated CLN3-deficient retinas after white-light exposure. (A) Iba1-stained retinal cryosections show less microglial migration towards the subretinal space 4 days after light exposure when mice are treated with minocycline during the white-light exposure regimen compared to vehicle-treated animals. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Less autofluorescent material in microglial cells is present 4 days after light exposure in minocycline-treated CLN3-deficient animals compared with vehicle-treated animals. A high amount of autofluorescent material and many microglial cells were present in the subretinal space of vehicle-treated animals at day 4. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C-E) Quantification of the Iba1-positive area (C), number of microglial cells (D) and area covered by autofluorescent material (E) showed significant reductions after minocycline administration in comparison to vehicle-treated animals 4 days and 7 days after light exposure. Data show mean±s.e.m. (n=24 pictures/group) from two independent experiments with ***P<0.001. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; Mino, minocycline.