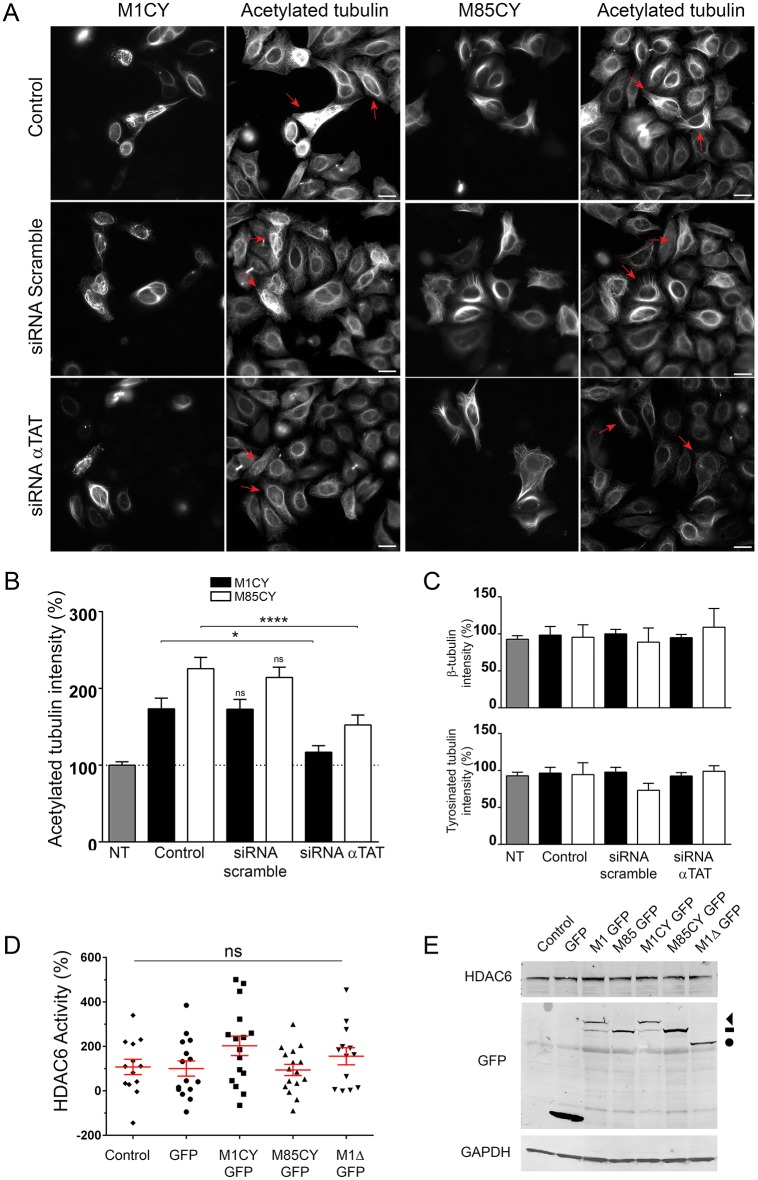
Fig. 5.
Spastin-induced tubulin acetylation depends on α-TAT activity. (A) HeLa cells were transfected for 24 h with siRNA against all isoforms of α-TAT or siRNA scramble, and co-transfected for 48 h with the same siRNA and GFP-tagged mutated spastin. Cells were fixed after 72-96 h of siRNA treatment and stained for acetylated tubulin. Red arrows indicate the effect of siRNA treatment on acetylated tubulin in mutated spastin-expressing cells. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Quantification of the average intensity of acetylated tubulin in the different experimental conditions. Data are normalized to untreated and nontransfected cells (100%). The number of cells analyzed ranged between 20 and 73. (C) Quantification of the average intensity of tyrosinated and β-tubulin in the same experimental conditions. (D) Quantification of HDAC6 catalytic activity. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-tagged spastin mutants, GFP as control or mock transfected (control), and the catalytic activity of the enzyme HDAC6 was measured using a HDAC6 activity fluorometric assay (Biovision), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Data are the average of 13-16 replicates from four independent experiments and represented as a percentage of the control condition. (E) Representative immunoblot of HeLa cells transfected with spastin GFP-tagged constructs. The expression level of HDAC6 protein was not altered by spastin expression. The arrowhead indicates M1CY-GFP, dash indicates M85CY-GFP and circle indicates M1Δ-GFP. Blot from Fig. 2C was stripped and re-probed for the proteins shown; the same control blot is used in both figures. Data are shown as mean±s.e.m. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's post test. *P<0.05; ****P<0.001; ns, not significant. NT, not treated.