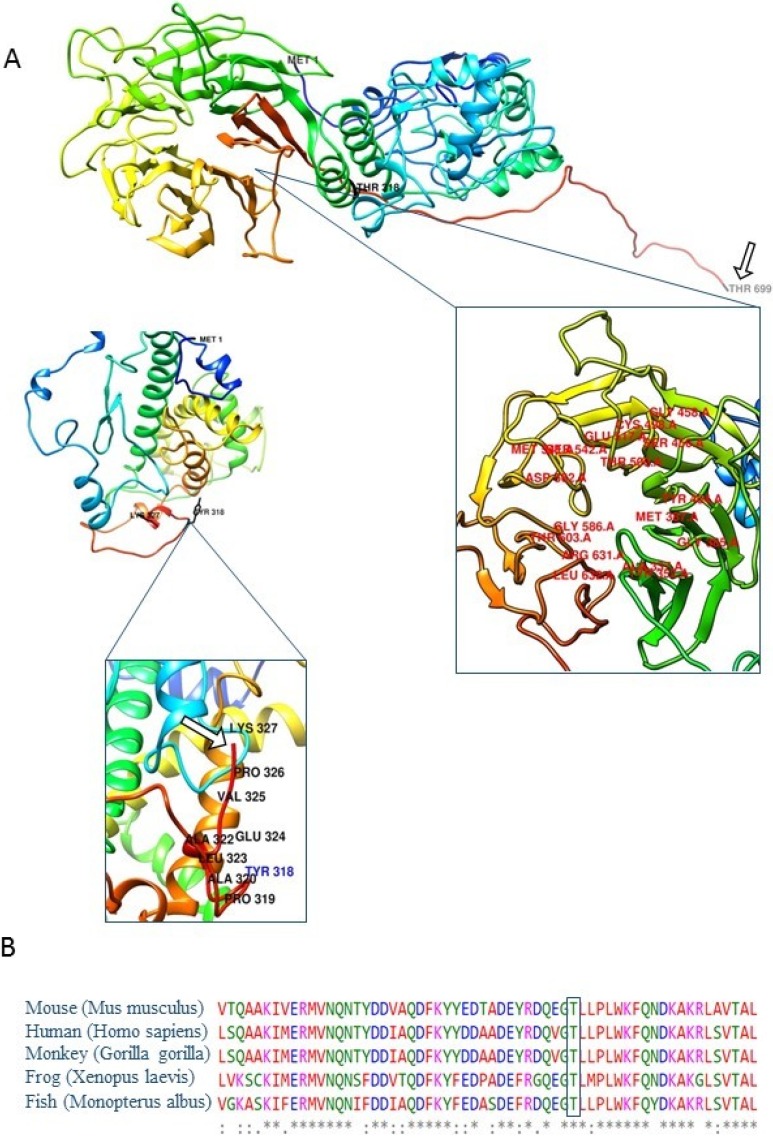
Fig 2. Three-dimensional molecular models of DNAI1 protein with close-up views of the regions harbouring novel frameshift genetic variant, and regions for PPIs.
(A) View of the wild type (top picture) and mutated (bottom picture) DNAI1 protein. Wild type DNAI1 protein consists of 699 amino acids (GenBank accession number: NP_036276.1). Mutated is shorter than wild type and consists of 327 amino acids. Proteins begin to differ after position 318 in polypeptide chains. White arrows point to the last amino acid in polypeptide chains (Thr 699 in wild type and Lys 327 in mutated protein). Labelled amino acids in close-up view of wild type protein are representing ligand binding sites. Close-up view of mutated protein is displaying the altered region and truncation of protein due to frameshift stop mutation. Insertion has led to changes in open reading frame and consequently incorporation of incorrect amino acids downstream of insertion and premature stop codon. Images were prepared using UCFS Chimera software (http://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimera). (B) Amino acid sequence alignment with ClustalW2. Five sequences were aligned and results indicate to high evolutionary conservation of residues affected by p.Thr318TyrfsTer11 variant among the DNAI1 orthologs in all analyzed vertebrate species (mouse, monkey, frog, fish and human). The amino acid marked with a rectangle displayed absolute evolutionary conservation among analysed species.