Figure 2.
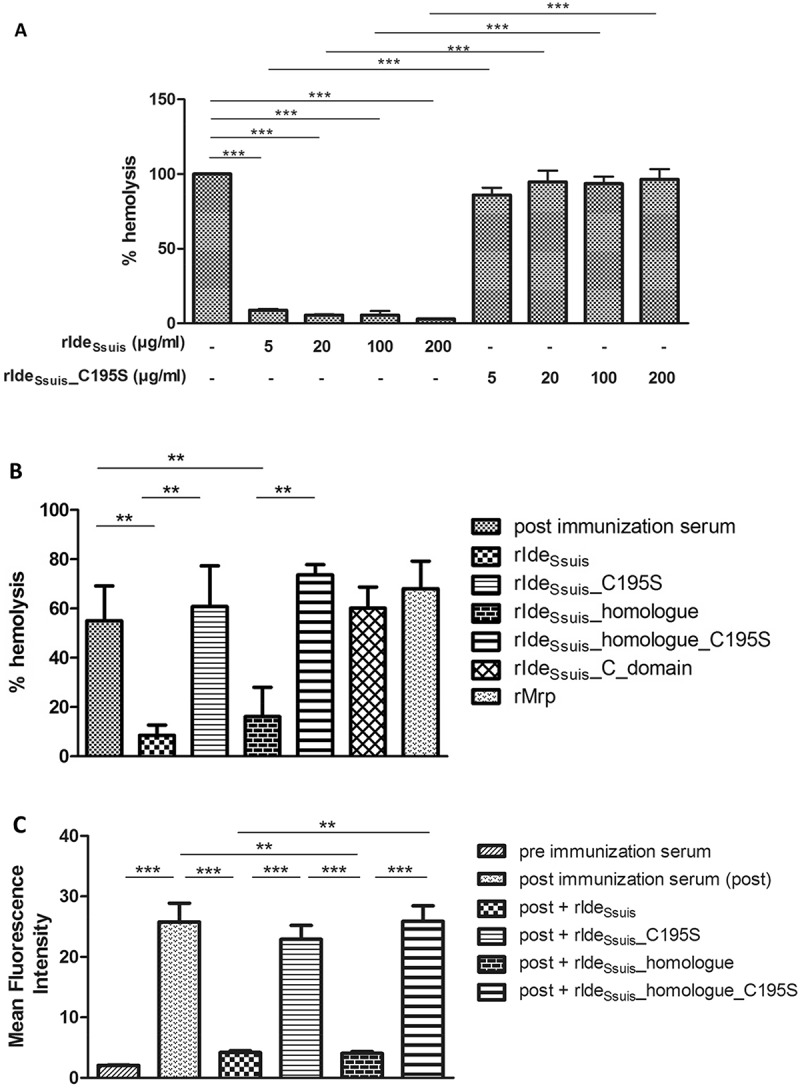
In the presence of high S. suis specific IgM titers, complement-mediated hemolysis and labeling of sheep erythrocytes with IgM are significantly reduced by rIdeSsuis constructs with IgM cleaving activity, but not by rIdeSsuis constructs lacking IgM cleavage activity due to the C195S point mutation. Hemolysis assays were performed by addition of purified sheep erythrocytes to pig anti-sheep erythrocyte serum which had been pretreated with either different concentrations of rIdeSsuis and rIdeSsuis_C195S (a) or different recombinant IdeSsuis constructs (b). The assays were performed with porcine serum drawn seven days after immunization with sheep erythrocytes (n = 4). Bars and error bars represent mean and standard deviation and significant differences are indicated. (a) Hemolysis induced by water was defined as one hundred percent and is represented by the first bar. (b) rIdeSsuis wt, rIdeSsuis_C195S, rIdeSsuis_homologue, rIdeSsuis_homologue_C195S, rIdeSsuis_C_domain, rMrp were compared regarding their ability to reduce complement mediated hemolysis at 18 µg/ml. Recombinant Mrp served as a control protein and was purified the same way as rIdeSsuis constructs. Post immunization serum without either rIdeSsuis construct served as negative control. (c) Flow cytometric analysis of IgM labeled sheep erythrocytes was performed after addition of purified sheep erythrocytes to a heat inactivated porcine anti-sheep erythrocyte serum drawn seven days after immunization and pretreated with 18 µg/ml of the indicated rIdeSsuis constructs. Serum drawn prior to immunization with sheep erythrocytes served as negative control. Serum drawn seven days post immunization served as positive control. Bars and error bars show mean values and standard deviations (n = 6). Significant differences are indicated by asterisks. Probabilities were considered as follows p < 0.05 *, p < 0.01 **, p < 0.001 ***.
