Figure 7.
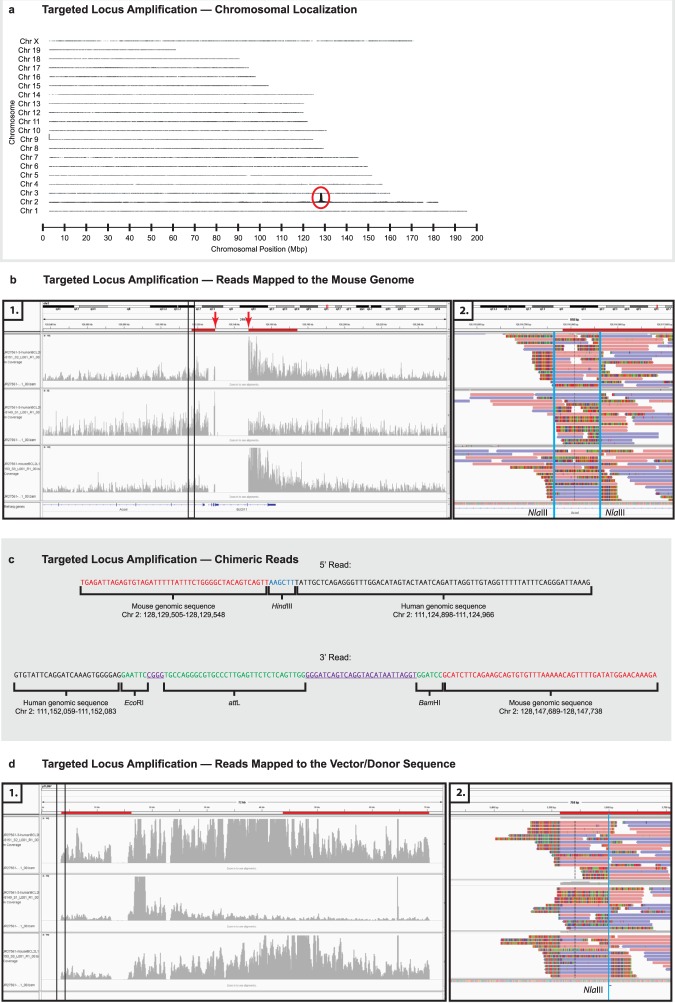
(a) Targeted Locus Amplification — Chromosomal Amplification. High-throughput sequencing reads, obtained through the use of the TLA technique with human and mouse BCL2L11-/Bcl2l11-derived target amplimers, identify distal Chr2 as the integration site of the humanizing gene targeting vector/donor molecule. This result is entirely consistent with integration of the human BCL2L11 segment within the endogenous mouse Bcl2l11 gene as designed (vertical axis, read-depth along each of the mouse chromosomes; horizontal axis, chromosomal position). (b) Targeted Locus Amplification — Reads Mapped to the Mouse Genome. 1. High-throughput sequencing reads, obtained through the use of the TLA technique with human and mouse BCL2L11-/Bcl2l11-derived target amplimers, localize to the mouse Bcl2l11 locus outside of the humanized region. This result is entirely consistent with integration of the human BCL2L11 segment within the endogenous mouse Bcl2l11 gene as designed (vertical axis, read-depth along the mouse Bcl2l11 locus for each of three target amplimers; horizontal axis, chromosomal position; red lines, regions of the two mouse homology arms; red arrows, internal boundary of homology arms and location of chimeric human/mouse BCL2L11/Bcl2l11 sequencing reads; central blue gene structure, Bcl2l11; left blue gene structure, an adjacent gene; narrow vertical rectangle, region examined in panel 2). 2. Sequencing reads mapping to the 5′ end of the 5′ homology arm/flanking mouse genome boundary. Sequencing reads spanning the homology arm/genome boundary are contiguous (horizontal pink and purple bands). Fusion reads (horizontal bands with multicolored segments) arise only from nearby NlaIII sites (NlaIII-labelled vertical blue lines) and are an artifact of the TLA technology. No fusion reads suggest integration at an ectopic locus. Analysis of the 3′ end of the 3′ homology arm was similar (not shown). (c) Targeted Locus Amplification — Chimeric Reads. Representative reads from the 5′ and 3′ mouse/human breakpoints (junctions) of the humanized BCL2L11/Bcl2l11 locus (red lettering, mouse-derived sequence; black lettering, human-derived sequence; blue lettering, vector-derived HindIII site at the 5′ mouse/human junction; green lettering, vector-derived EcoRI, attL, and BamHI sites at the 3′ mouse/human junction; underlined purple lettering, additional vector-derived sequences). (d) Targeted Locus Amplification — Reads Mapped to the Vector/Donor Sequence. 1. High-throughput sequencing reads, obtained through the use of the TLA technique with human and mouse BCL2L11-/Bcl2l11-derived target amplimers, localize across the pTLD67 gene targeting vector/donor molecule including mouse and human elements. This result is entirely consistent with integration of the human BCL2L11 segment within the endogenous mouse Bcl2l11 gene as designed (vertical axis, read-depth along the pTLD67 vector for each of three target amplimers; horizontal axis, position within the vector; red lines, regions of the two mouse homology arms; narrow vertical rectangle, region examined in panel 2). 2. Sequencing reads mapping to the 5′ end of the 5′ homology arm/vector boundary. Reads arising from the point of integration (horizontal bands with multicolored segments) appear as fusion reads at the homology arm/vector boundary. Additional fusion reads arise only from a nearby NlaIII site (NlaIII-labelled vertical blue line) and are an artifact of the TLA technology. No fusion reads suggest continuity into the vector’s backbone. Analysis of the 3′ end of the 3′ homology arm was similar (not shown).