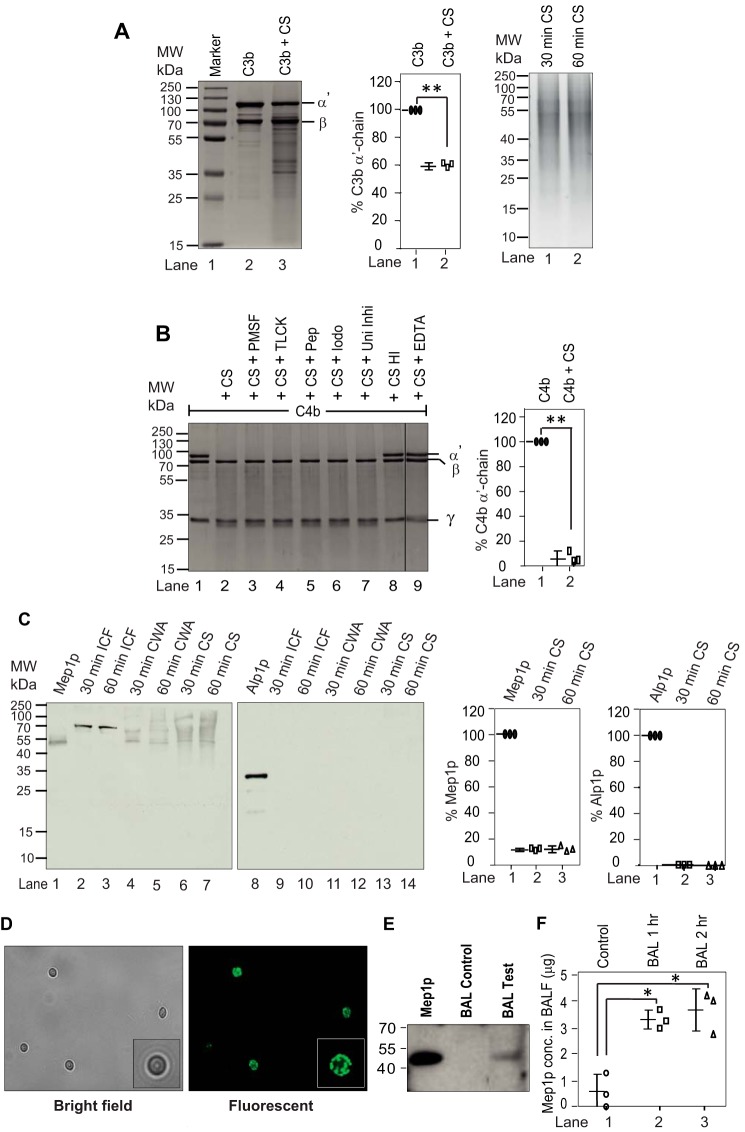
Figure 1.
Cleavage of complement proteins by A. fumigatus culture supernatant and secretion of proteases from A. fumigatus conidia in collagen-containing medium. A, cleavage of C3b by A. fumigatus culture supernatant (CS). C3b (2 μg) was incubated for 60 min at 37 °C with the CS (1 μg of protein) obtained after 60 min of conidial inoculation in Tris buffer, pH 7.4 (total reaction volume of 30 μl). The reaction mixtures were then run on 10% SDS-PAGE, and the cleaved fragments of C3b were visualized by staining the gel with Coomassie Blue (left panel). The middle panel shows the % cleavage of C3b α′-chain by CS. Data represent mean ± S.D. of three experiments (**, p < 0.005). The right panel shows the CS collected at 30 and 60 min. B, cleavage of C4b by A. fumigatus CS and its inhibition by various protease inhibitors. C4b (2 μg) was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C with the CS (1 μg of protein) obtained after 60 min of conidial inoculation in Tris buffer, pH 7.4 (total reaction volume of 30 μl). The reaction mixtures were then run on 10% SDS-PAGE, and cleaved fragments of C4b were visualized by staining the gel with Coomassie Blue (left panel). The splice line between the lanes 8 and 9 indicates that the gel was spliced at this point. Inhibitors used are as follows: PMSF, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (1 mm); TLCK, tosyl-l-lysyl-chloromethane hydrochloride (1 mm); Pep, pepstatin (11 μg/ml); Iodo, iodoacetamide (1 mm); Uni Inhi, universal inhibitor without EDTA (1×); EDTA, (10 mm). HI indicates heat-inactivated. CS effectively cleaved C4b, which could be inhibited by EDTA suggesting the involvement on metalloprotease in C4b cleavage. The right panel shows the % cleavage of C4b α′-chain by CS in the presence of the indicated inhibitor (**, p < 0.005). Data represent mean ± S.D. of three experiments. C, A. fumigatus conidia were cultured in collagen-containing medium for 30 min or 60 min. The CS was then collected, and the conidia were broken open to collect the intracellular fraction (ICF) and the cell wall autolysate (CWA). The intracellular fraction contained Mep1p in the pro-form (70 kDa), and the cell wall fraction and the culture supernatant contained Mep1p in the activated form (42 kDa); none of the fractions contained Alp1p (left panels). The right panels show % release of Mep1p and Alp1p compared with the control lane (1 μg of Mep1p or Alp1p). Data represent mean ± S.D. of three experiments. D, detection of Mep1p in the permeabilized conidia by immunofluorescence. E, Mep1p in BALF of mice after exposure to WT conidia for 2 h. Released Mep1p was detected by Western blot analysis using polyclonal anti-Mep1p antibody. F, Mep1p in BALF is also quantified by ELISA (mean ± S.D. of three experiments; values represent the Mep1p concentration in 5 ml of BALF collected from each mouse; *, p < 0.05).