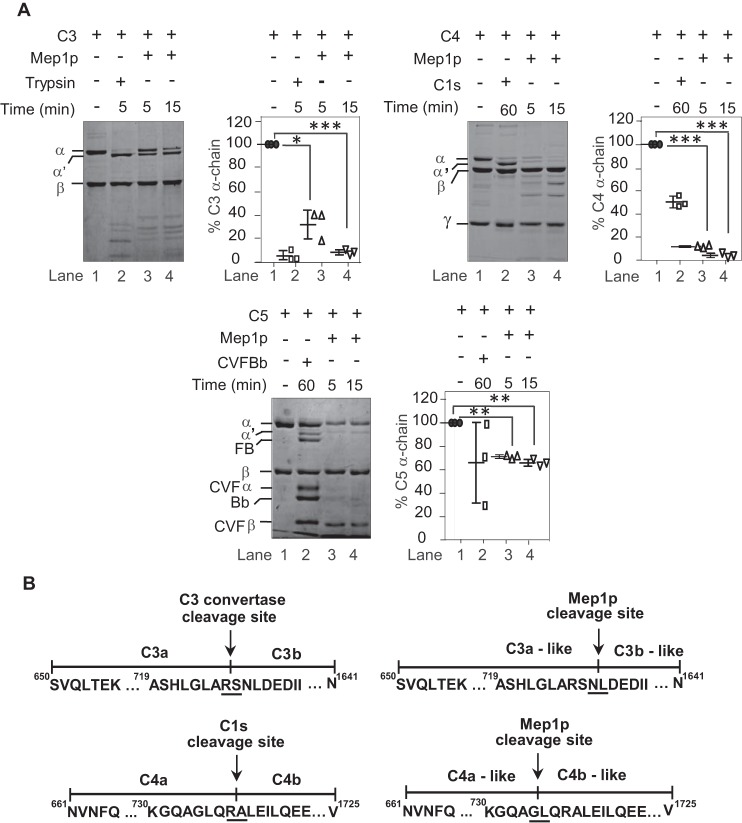
Figure 5.
Proteolytic activity of Mep1p toward C3, C4, and C5. A, cleavage of C3, C4, and C5 by Mep1p. Three micrograms of purified C3, C4, or C5 were incubated with 0.5 μg of Mep1p in Tris buffer for the indicated time period at 37 °C and analyzed on SDS-PAGE. The reactions were run on 7.5, 9, and 6% SDS-PAGE for C3, C4, and C5, respectively, under reducing conditions. The controls were formed by incubating C3 with trypsin or C4 with C1s or C5 with CVF Bb, i.e. C5 convertase. Mep1p converts C3, C4, and C5 into C3b-/C3a-like, C4b-/C4a-like, and C5b-/C5a-like fragments. The panels on the right side of each gel show % cleavage of α-chains of the respective protein. Data represent mean ± S.D. of three experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005). B, identification of the Mep1p cleavage site on C3 and C4 by N-terminal sequencing of the cleaved α′-chains. The α′-chains of C3b-like and C4b-like obtained after the Mep1p cleavage as described in A were subjected to N-terminal sequencing. The panels show the cleavage site for the respective convertases and Mep1p on C3 (upper sequences) and C4 (lower sequences). Mep1p cleaved C3 and C4 close to their physiological cleavage site by the respective convertases. Molecular weights: C3 α-chain, 110,000; C3 β-chain, 75,000; C4 α-chain, 97,000; C4 β-chain, 75,000; C4 γ-chain, 33,000; C5 α-chain, 115,000; C5 β-chain, 75,000; FB, 93,000; Bb, 60,000; CVF α-chain, 68,000; CVF β-chain, 48,000.