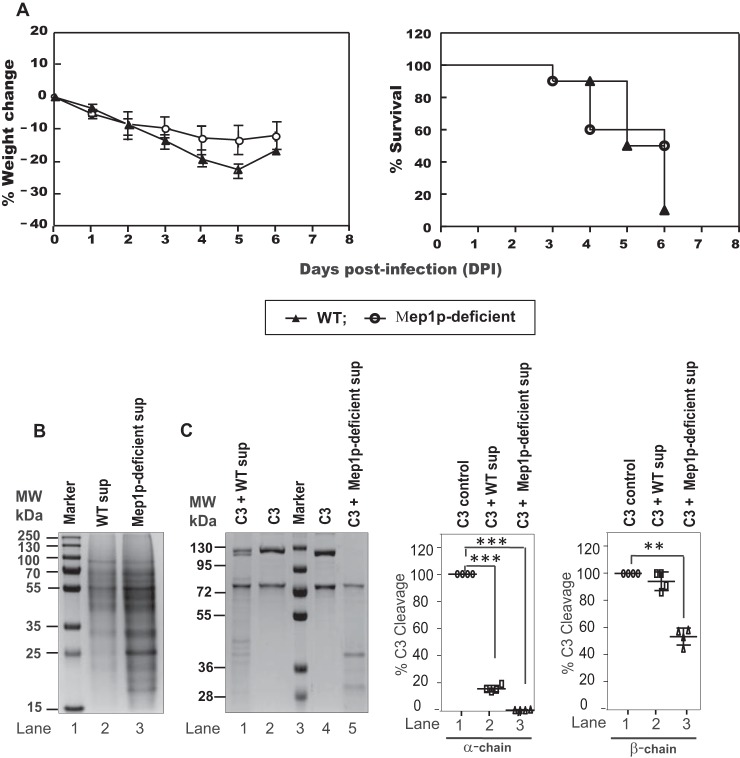
Figure 9.
Virulence of Mep1p-deficient and WT strain in cyclophosphamide-treated murine infection model. A, weight loss and survival of cyclophosphamide-immunosuppressed mice challenged with WT or Mep1p-deficient conidia (10 mice per group and two replications; totally 20 mice per group). Mice with weight loss of more than 30% of its original weight were sacrificed and considered dead for calculations of mortality. Although the survival was higher in the mouse group challenged by Mep1p-deficient (50%) compared with the mouse group challenged by WT (10%) conidia, the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.28; log-rank test). B, SDS-PAGE showing secreted protein profiles of WT and Mep1p-deficient mutant in the collagen culture supernatant. The gel was stained using Coomassie Blue. C, SDS-PAGE showing degradation of C3 α- as well as β-chain by WT and Mep1p-deficient conidial collagen culture supernatant. In this experiment, C3 was incubated with culture supernatant for 1 h at 37 °C. The right panels show the percent cleavage of C3 α- and β-chains by WT and Mep1p-deficient culture sup (mean ± S.D. of three experiments; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005).