Figure 1.
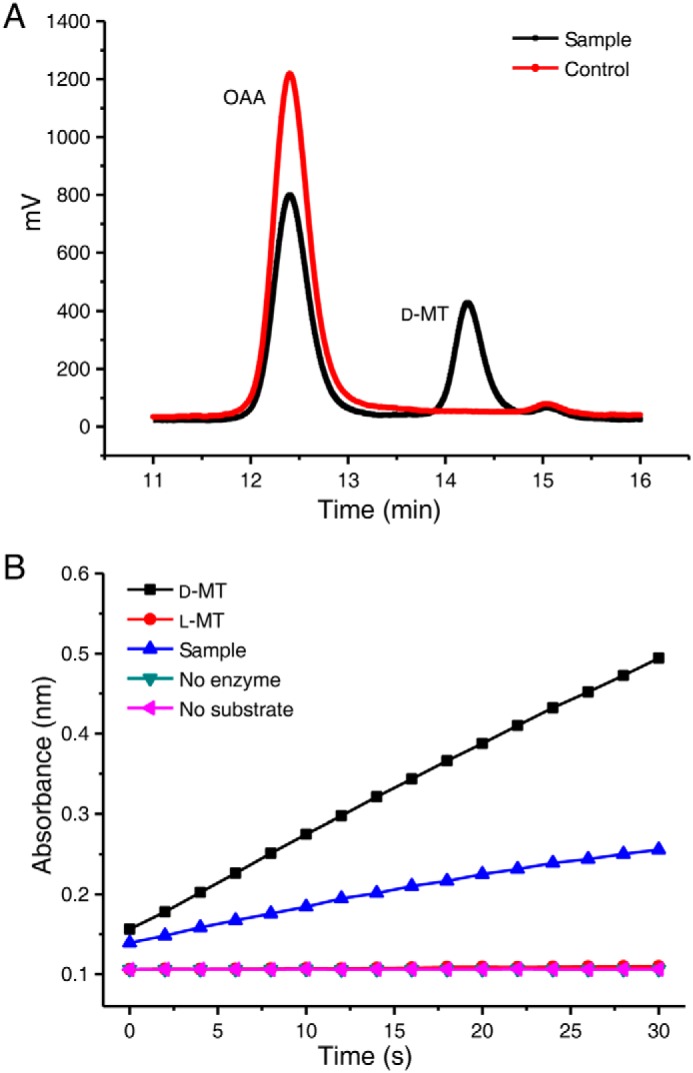
SerA can catalyze the production of d-malate from OAA. A, HPLC analysis of the product of SerA-catalyzed OAA reduction in the presence of NADH. Control, the reaction mixture containing OAA (2.5 mm), NADH (4 mm), heat-inactivated SerA (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 1 h. Sample, the reaction mixture containing OAA (2.5 mm), NADH (4 mm), active SerA (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 1 h. B, enzymic assay of the SerA-produced malate using d-malate dehydrogenase of E. coli. The reactions using authentic d-malate, l-malate, or SerA-produced malate as substrates were conducted using a UV-visible spectrophotometer. Sample, the product of SerA-catalyzed OAA reduction in the presence of NADH. The reactions without addition of substrate (no substrate) or d-malate dehydrogenase of E. coli (no enzyme) were used as the controls. d-MT, d-malate; l-MT, l-malate.
