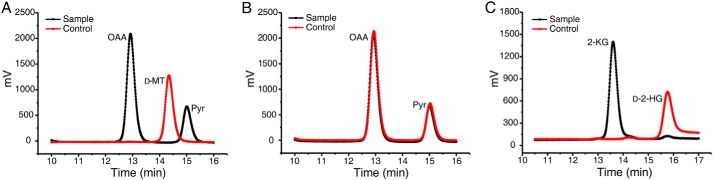
Figure 4.
D2HGDH catalyzes the α-dehydrogenation of d-malate to OAA and d-2-HG to 2-KG. A, the HPLC analysis of the product of D2HGDH-catalyzed d-malate conversion in the presence of MTT. Control, the mixtures containing d-malate (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), heat-inactivated D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. Sample, the mixtures containing d-malate (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), native D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. B, D2HGDH did not have OAA-decarboxylating activity. Control, the mixtures containing OAA (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), heat-inactivated D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. Sample, the mixtures containing OAA (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), native D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. C, the HPLC analysis of the product of D2HGDH-catalyzed d-2-HG conversion in the presence of MTT. Control, the mixtures containing d-2-HG (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), heat-inactivated D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. Sample, the mixtures containing d-2-HG (2.5 mm), MTT (4 mm), native D2HGDH (4.5 μm) in 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), incubated at 30 °C for 30 min. d-MT, d-malate; Pyr, pyruvate.