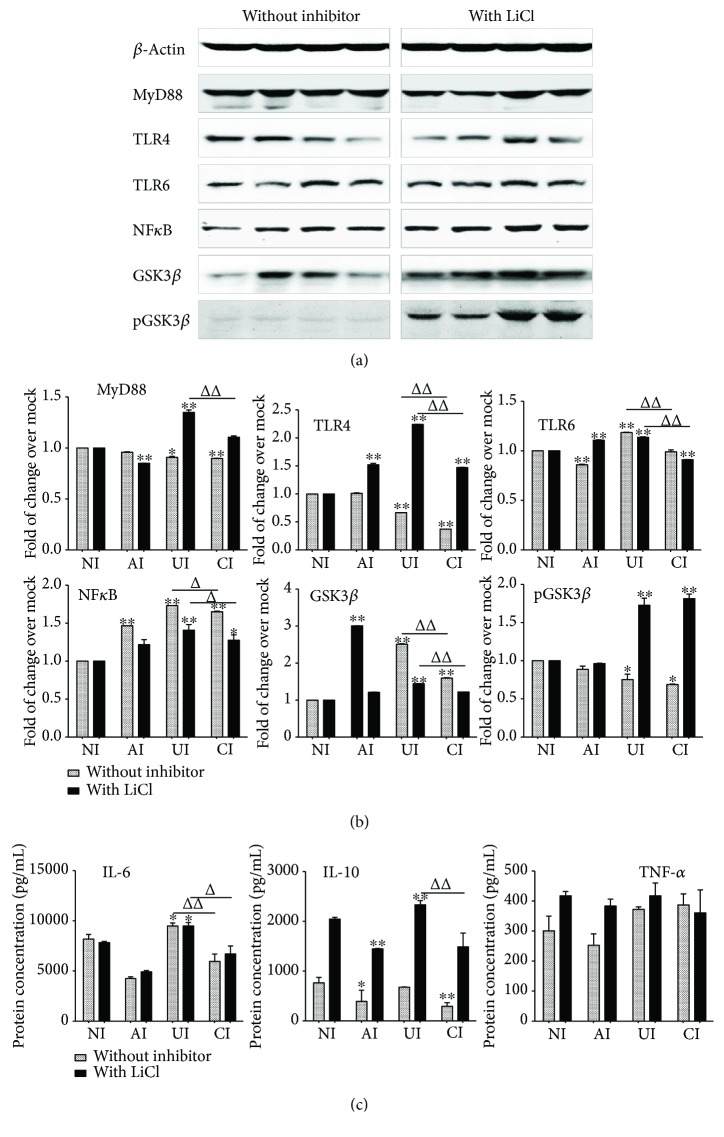
Figure 7.
Impact of GSK3β on the expression of TLR ligands and elements of the TLR signaling pathway in U937 cells to Mtb H37Rv infection in the A549 cell coculture model. In the presence or absence of GSK3β inhibitor LiCl, the coculture model of A549/U937 cells was infected with H37Rv mycobacteria from the upper chamber (A549 cells, AI), lower chamber (U937 cells, UI), or both chambers (A549 and U937 cells, CI) at a MOI of 3 for 18 h before the culture medium and U937 cells were harvested for analysis. (a) Representative blots of immunoblotting assay for indicated components of TLR signaling cascade showed an activated TLR signaling in U937 cells of the coinfection model in the presence of LiCl, in comparison with the absence of an inhibitor. (b) The fold of changes of proteins of interest in (a) semiquantitatively determined by densitometric assay using ImageJ software Fiji from three independent experiments. (c) Concentrations of TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-6 in culture media determined by ELISA. An augmented cytokine production was observed in the presence of GSK3β inhibitor LiCl, but the trend of a reduced TLR-mediated inflammatory response was not altered by the addition of LiCl. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments. Compared to noninfection (NI) control, ∗ p < 0.05 and ∗∗ p < 0.01; compared to the absence of LiCl, Δ p < 0.05 and ΔΔ p < 0.01. NI: noninfected control; AI: infection was performed on A549 cell alone; UI: infection was performed on U937 alone; CI: infection was performed on both A549 cells and U937 cells.