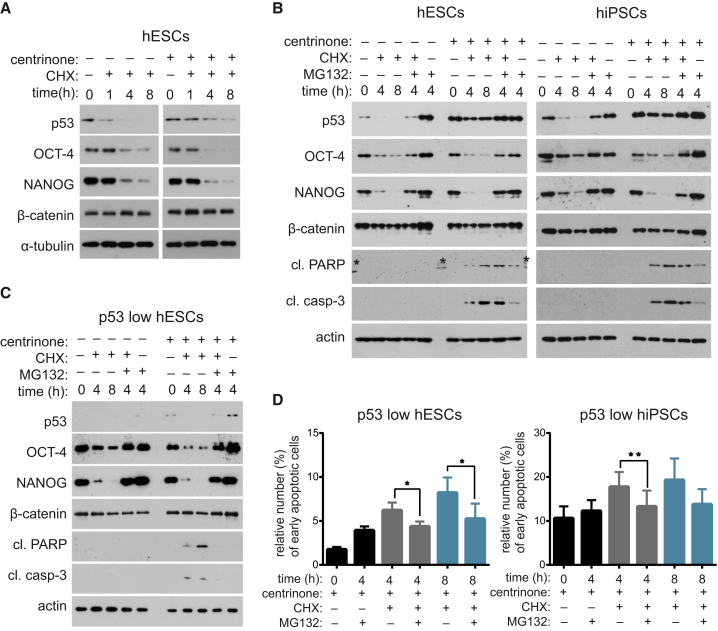
Figure 5.
Loss of Pluripotency after PLK4 Inhibition and Centrosome Depletion Is Linked to Altered Protein Turnover
hESCs (mock: A and B, or p53 low: C and D) and hiPSCs (mock: B, or p53 low: D) were treated with centrinone (2 days) and indicated chemicals, and analyzed by western blot for protein expression (A–C) or by annexin V/PI staining for apoptosis (D).
(A) Western blot analyses of centrinone treatment effect on protein turnover after block of protein synthesis for indicated time by cycloheximide (CHX). Note the increased turnover of OCT-4 and NANOG, and the decreased turnover of p53 in centrinone conditions. β-Catenin was included in all depicted experiments as additional control for specificity; α-tubulin/actin served as loading controls.
(B and C) Analysis of rescue effects of inhibition of proteasome (MG132) on altered protein turnover following centrinone treatment (B). Where indicated, CHX was added together with MG132 for indicated time to analyze turnover rate of p53, OCT-4, NANOG, and β-catenin. Cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 were used to probe for apoptosis (asterisks show non-specific antibody binding to marker). (C) Analysis of p53 low hESCs.
(D) Viability measurement by annexin V/PI staining of p53 low hESCs/hiPSCs in the indicated conditions (hESCs, n = 4; hiPSCs, n = 3).
Data are presented as mean ± SEM (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005). See also Figure S4.