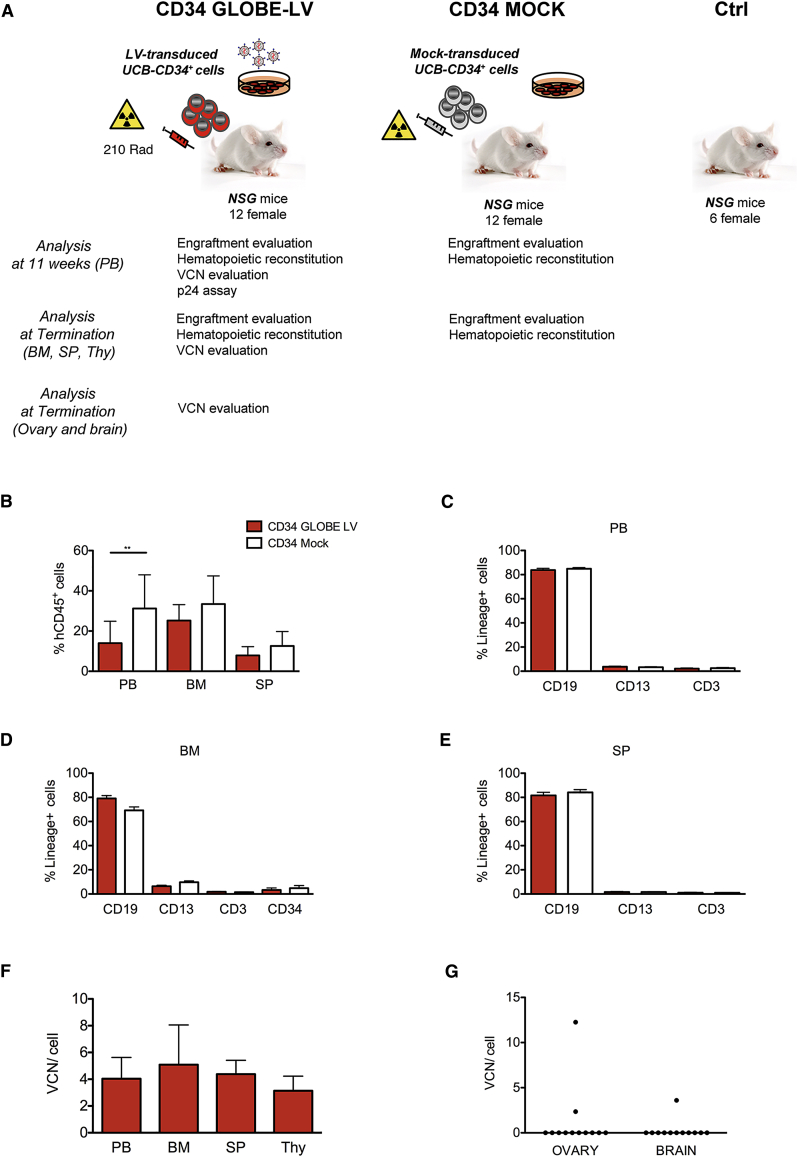
Figure 5.
Biodistribution Study in the Human Chimera Murine Model
(A) Experimental plan of the biodistribution study. Female NSG (NOD.Cg-Prkdcsid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ) recipient mice were conditioned by a sub-lethal dose of irradiation to provide depletion of endogenous BM cells, allowing engraftment of human cells. After conditioning, NSG GLOBE LV mice (n = 12) were intravenously injected with transduced CD34+ cells, NSG MOCK mice (n = 12) were treated with MOCK-transduced cells, and NSG control mice (n = 6) were left untreated and served as controls. At the end of the study, the engraftment, the differentiation to specific lineages, and the persistence of transduced human cells in hematopoietic organs were evaluated. After extensive perfusion to eliminate contaminating blood, gonads and brain were analyzed by qPCR to evaluate the distribution of human cells in non-hematopoietic organs. HIV p24 was assayed in mouse serum to test for the absence of replication-competent lentivirus. (B) Analysis of hematological reconstitution was assessed by cytofluorimetric analysis in PB, BM, and SP by using anti-human CD45+ (**p < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t test ). (C–E) PB (C), BM (D), and SP (E) showed multi-lineage differentiation of lymphoid and myeloid cells (CD19+, CD3+, and CD13+) both in transduced and MOCK-transduced cells. (F) VCN per cell was determined in PB, BM, SP, and thymus by qPCR. (G) VCN per cell was determined in ovaries and brain. All values are shown as mean ± SD.