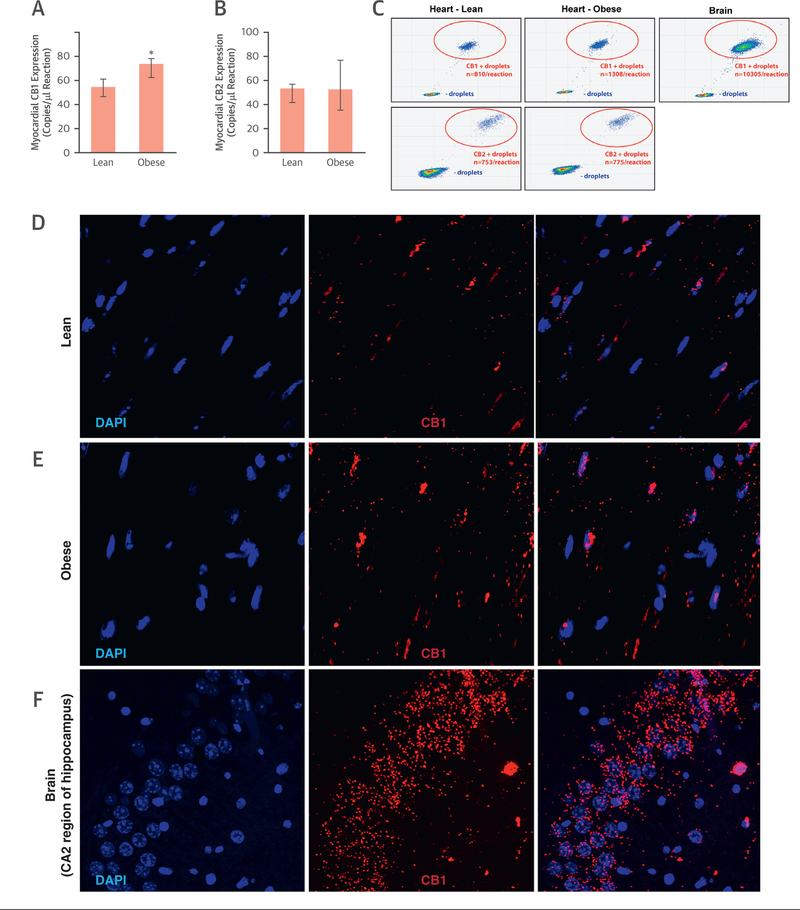
FIGURE 3. Myocardial Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor Expression in Mice.
(A) Expression of myocardial cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1-R), expressed as copies per microliter of the droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) in lean and obese mice (n = 3); *p ≤ 0.05. (B) Expression of myocardial cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB2-R), expressed as copies per microliter of the ddPCR in lean and obese mice. (C) Representative ddPCR fluorescence-activated cell sorting plots of CB1-R and CB2-R expression in hearts of lean and obese mice and in the mouse brain (positive control for CB1-R) (B). Each panel represents a single ddPCR experiment whereby a deoxyribonucleic acid sample was segregated into individual droplets and assessed for the presence of CB1-R and CB2-R complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Droplets in the bottom left quadrant represent negative droplets, while droplets in the top right quadrant are positive droplets, each droplet containing a single copy of the CB1-R and CB2-R, respectively. Confocal microscopic imaging of CB1-R messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) by RNAscope in situ hybridization in lean (D) and obese (E) mouse hearts, as well as in the CA2 region of mouse hippocampus (F). 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining (blue) shows nuclear structure, and CB1 staining (Cy3; red) shows localization of CB1 mRNA.