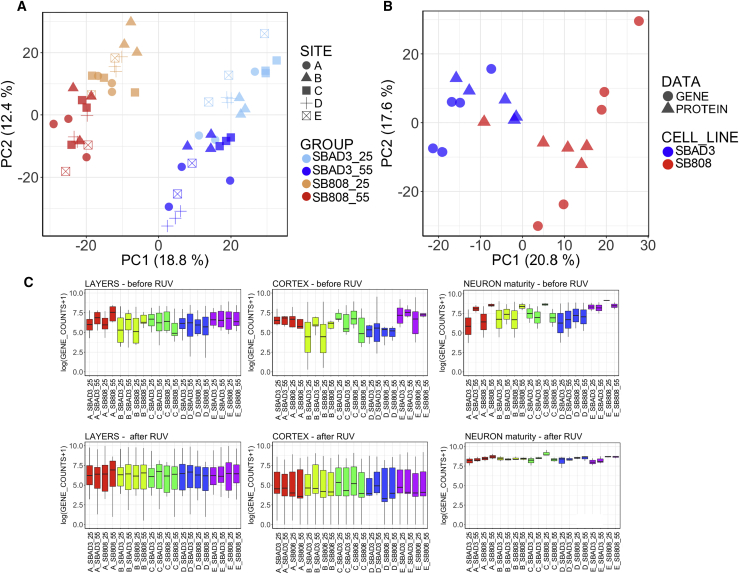
Figure 4.
Impact of Unwanted Variance Removal by RUV Correction
(A) RUV separates sample gene expression profiles by cell line and time point. First two principal components from a PCA on gene expression over all samples after RUV correction.
(B) RUV separates sample gene expression and protein abundance profiles by cell line. First two principal components from a “second” PCA on both pooled gene and protein expression adjusted for PC1 of “first” PCA. This first PC1 captures the differences between protein and gene expression, therefore adjustment makes the two datasets more comparable. Gene expression values and protein abundances are RUV corrected separately on the two datasets for FP + 55 time point.
(C) RUV normalizes the expression of marker genes expected to be similarly expressed across all samples. Gene expression on log scale of gene markers of three neuron-specific stages before (top row) and after RUV correction (bottom row). Box-and-whisker graphs represent distributions, where the span of the box is the interquartile range (IQR) and includes the median (bold line). The ends of the upper and lower whiskers represent the data point with the maximum distance from the third and first quartiles, respectively, but no further than 1.5 × IQR. Data beyond the end of the whiskers are outliers.