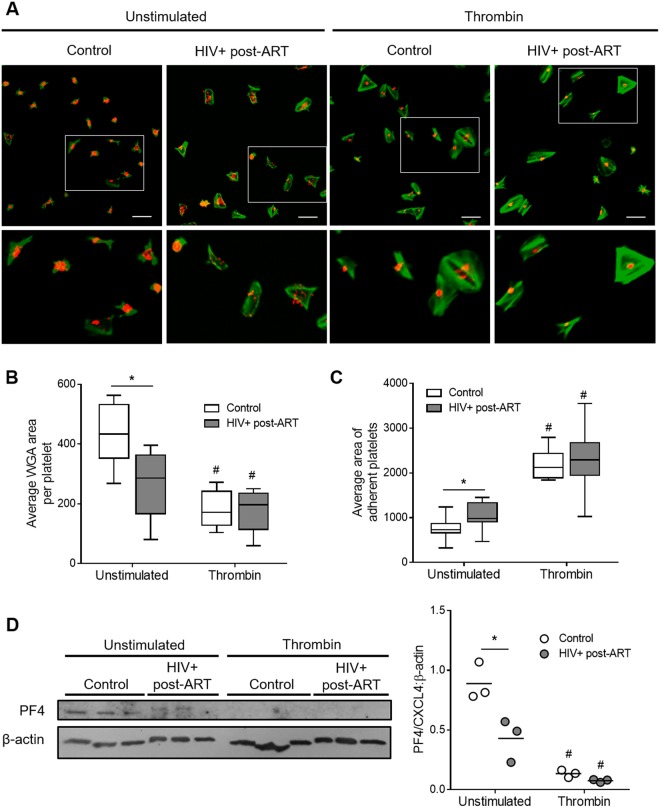
Figure 4.
Thrombin-induced platelet spreading and degranulation in HIV-infected individuals under stable cART and healthy volunteers. (A) Platelets from healthy subjects (control) or HIV-infected individuals under viral control (HIV-1 viral load < 50 copies/ml in the peripheral blood) were stimulated with thrombin (0,0 or 0,4 U/mL), adhered to fibrinogen-coated surfaces and labeled with phalloidin (green) and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA – red) as described in methods. (B) Average area of WGA labeling per platelet number in each field for unstimulated or thrombin-stimulated platelets from control or HIV-1-infected subjects. (C) Average area of spontaneous or thrombin-induced platelet spreading on fibrinogen-coated surfaces in each condition. Images are representative of eight HIV-infected individuals and healthy volunteers analyzed in parallel. Scale bars represent 10 µm. The horizontal lines on the box plots represent the median, boxes limits indicate interquartile ranges and the whiskers indicate 5–95 percentile. (D) Western blot analysis for PF4/CXCL4 and β-actin in platelets from three healthy volunteers and three HIV-infected subjects under stable cART that were kept unstimulated or stimulated with 0.4 U/mL of thrombin. Dots represent the band intensity of PF4 corrected by β-actin expression in each experimental condition. Horizontal lines represent mean. The asterisk (*) signify p < 0.05 compared to healthy volunteers and # means p < 0.05 compared to unstimulated platelets.