Figure 1.
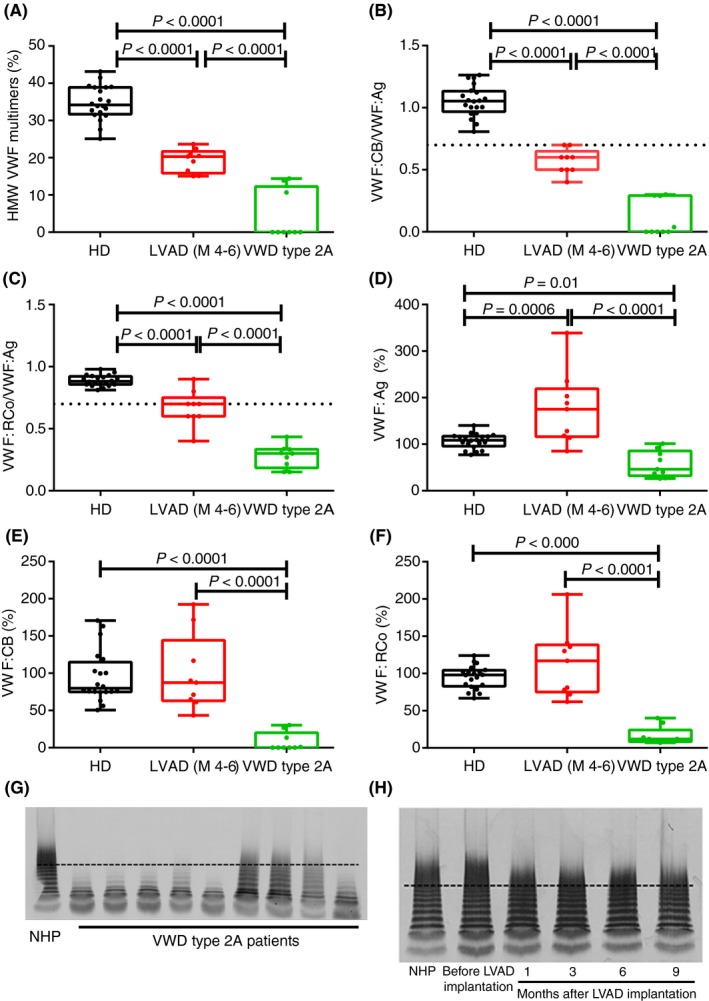
HMW VWF multimers, VWF antigen, VWF collagen binding activity and VWF ristocetin cofactor activity in VWD type 2A and LVAD‐induced aVWS patients. HMW VWF multimers, VWF antigen (VWF:Ag), VWF collagen binding activity (VWF:CB) and VWF ristocetin cofactor activity (VWF:RCo) were determined in healthy donors (HD, n = 20), patients with VWD type 2A (n = 9) and in LVAD‐induced aVWS patients (n = 9). (A) HMW VWF multimers were severely reduced in VWD type 2A patients and decreased in LVAD‐induced aVWS patients at 4 to 6 (M 4‐6) months after LVAD implantation. HD were used as control samples. (B) The ratio of VWF:CB over VWF:Ag (VWF:CB/VWF:Ag) and (C) VWF:RCo over VWF:Ag (VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag) was severely decreased in all VWD type 2A patients but not in LVAD‐induced aVWS patients. VWF:Ag (D), VWF:CB (E) and VWF:RCo (F) was decreased in VWD type 2A patients but not in LVAD‐induced aVWS patients compared to HD. Representative VWF multimeric pattern of (G) VWD type 2A patients and NHP (normal human plasma) and (H) an LVAD‐induced aVWS patient before LVAD implantation and 1,3,6 and 9 months after implantation of the LVAD and NHP (the proportion of HMW VWF multimers are situated above the dashed line). Percentages and ratios are represented as a boxplot with the median and interquartile ranges (25th and 75th percentile). LVAD, left ventricular assist devices; NHP, normal human plasma; VWF, von Willebrand factor; VWS, von Willebrand syndrome
