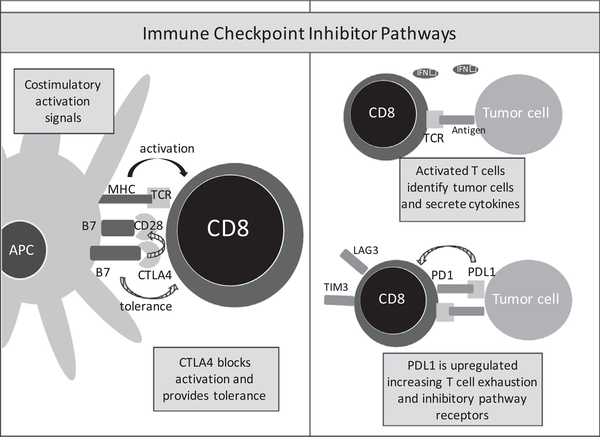
Fig. 2.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor pathways decrease T cell function, inhibit activation, and differentiation to prevent excessive inflammation. CTLA4 binds to the B7 complex of antigen-presenting cells (APC) blocking the costimulatory activation signal. PD1/PDL1 plays a role in the initiation of T cell exhaustion and upregulation of other inhibitory pathway receptors such as LAG3 or TIM3.