Figure 4. Vascular access of MCMV-driven memory NK cells.
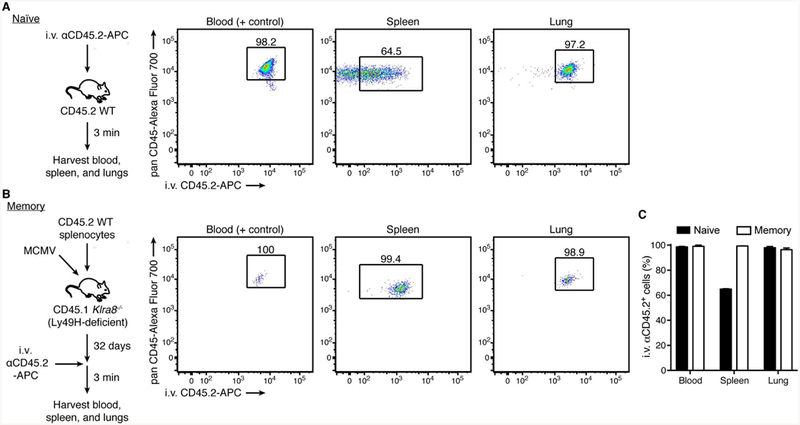
(A) Experimental schematic (left). Intravascular leukocytes of C57BL/6 mice were labeled with APC-conjugated anti-mouse CD45.2 antibody, as described in Figure 2. Representative flow plots of intravascular-labeled naïve Ly49H+ NK cells (CD45+TCRβ-CD3-NK1.1+Ly49H+) in indicated organs (right).
(B) Experimental schematic (left). Splenocytes from WT CD45.2 mice were adoptively transferred intravenously into Ly49H-deficient CD45.1 recipients one day prior to MCMV infection by intraperitoneal injection. On day 32 post-infection (memory), intravascular leukocytes were labeled with APC-conjugated anti-mouse CD45.2 antibody. Representative flow plots of intravascular-labeled memory Ly49H+ NK cells in indicated organs (right).
(C) Quantification of the percentage of naïve or memory Ly49H+ NK cells staining positive for i.v. αCD45.2 in indicated organs. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.
