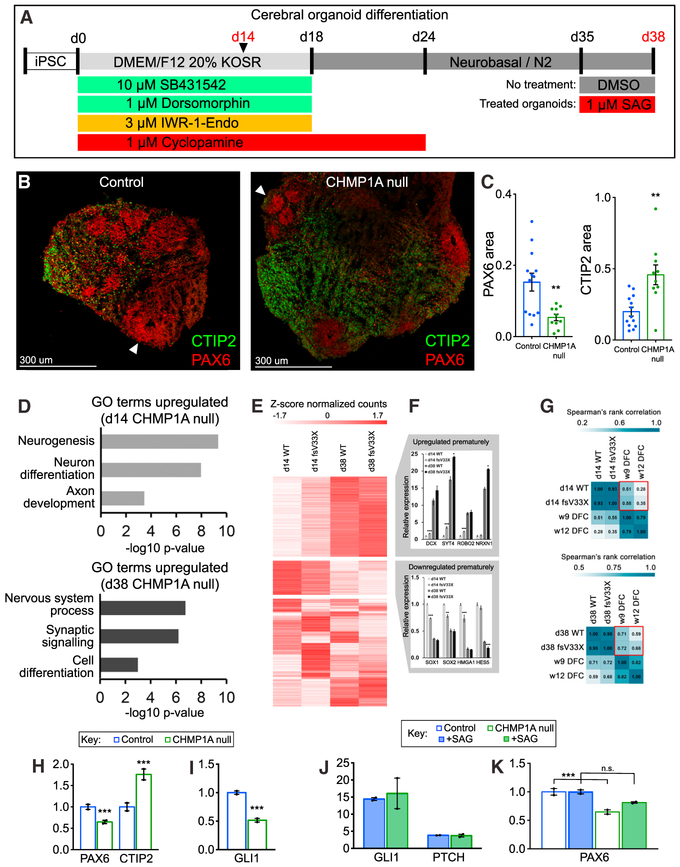
Figure 4. CHMP1A Is Essential for Progenitor Maintenance in Human Cerebral Organoids.
(A) Human cerebral organoid differentiation protocol.
(B) Organoids contain cortical progenitors (red, immunostained for PAX6, arrowheads) surrounded by postmitotic neurons (green, immunostained for CTIP2).
(C) PAX6 area is decreased and CTIP2 area is increased in CHMP1A null organoids. Control, n = 13; Chmp1a null, n = 10.
(D) GO pathway enrichment analysis.
(E) RNA sequencing reveals clusters of genes up-and downregulated in CHMP1A null organoids.
(F) Expression of differentiation and postmitotic neuron markers is increased in CHMP1A null organoids, whereas expression of proliferative markers is decreased.
(G) Comparison of organoid gene expression profiles to expression profiles of human fetal cortex.
(H) Decreased PAX6 expression and increased CTIP2 expression by RNA sequencing at day 38 in CHMP1A null organoids.
(I) Decreased GLI1 expression in CHMP1A null iPSCs.
(J) SAG treatment of organoids induces GLI1 and PTCH expression.
(K) SAG treatment partially rescues decreased PAX6 expression in CHMP1A null organoids.
(C and J) Two-tailed, unpaired t test. (F, H, I, and K) DESeq2 adjusted p value (Wald test).
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Error bars are SEM.