Figure 7. SHH Is Secreted on a Specific EV Subtype, ART-EV.
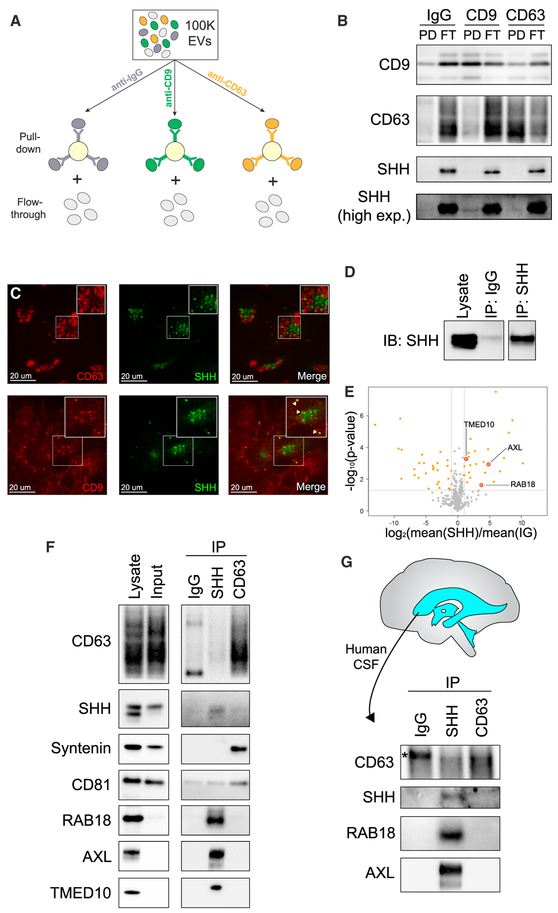
(A)Scheme of exosome isolation from the 100Kpellet by immunoprecipitation using beads coupled to CD9 and CD63 antibodies or mouse pan-immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. Both bound (pull-down) and unbound (flow-through) material was recovered.
(B) Representative WB of the bound (PD) and unbound (FT) fractions from exosome immunoisolation, probed with antibodies against CD9, CD63, and SHH (n = 3). Most SHH does not co-purify with exosomes but remains in the FT fraction.
(C) Immunostaining of exosomal markers CD9 or CD63 in cells ectopically expressing mNeonGreen-SHH.
(D) SHH-positive vesicles were purified from the 100K pellet by immunoisolation using anti-SHH antibodies.
(E) Peptides enriched in EVs isolated by SHH immunoisolation.
(F) Immunoisolated SHH-positive vesicles and CD63-positive exosomes were subjected to WB analysis, confirming the exclusive presence of RAB18, AXL, and TMED10 in purified SHH vesicles (n = 3). In contrast, Syntenin is only found on CD63-positive exosomes, while CD81 is present on both types of vesicles.
(G) SHH- and CD63-positive vesicles from the 100K pellet were immunoisolated from human CSF and subjected to WB analysis, confirming the exclusive presence of RAB18 and AXL on ART-EVs in vivo.
* indicates non-specific band.