Fig. 3. Free water as a robust marker of aging.
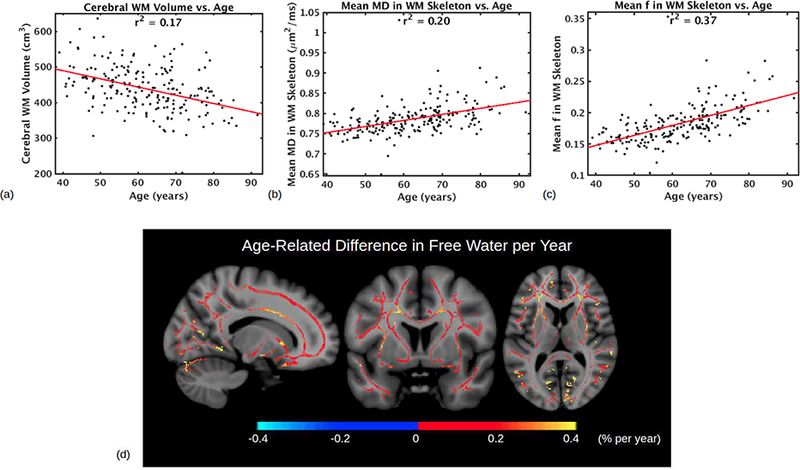
(a)-(c) compares different plots which aim to summarize WM degeneration with age. (a) Cerebral WM volume (cm3) vs. age, as calculated by FreeSurfer during cortical reconstruction. r = −0.4097, moderate correlation. (b) WM skeleton average of mean diffusion (MD, mm2/s) vs. age, as calculated from conventional DTI without FWE. r = 0.4503, moderate correlation. (c) WM skeleton average free water fraction f vs. age. r = 0.6052, strong correlation. (d) Significant positive association of free water fraction f with age in WM voxels. Color scale denotes the age-related difference in intravoxel free water percentage per year. The increase is more apparent in anterior regions than posterior regions. Abbreviations: DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; FWE, free water elimination; MD, mean diffusivity; WM, white matter.
