Fig. 7.
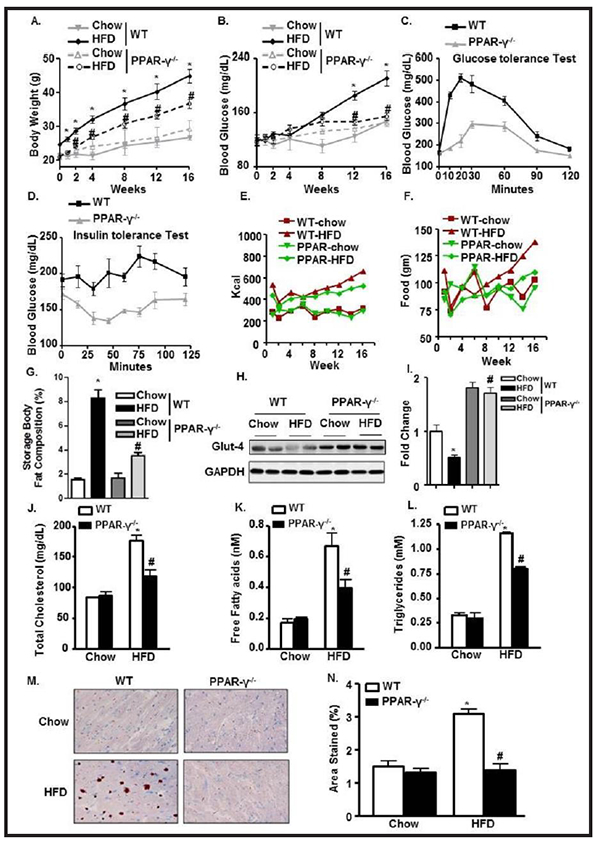
PPAR-γ ablation ameliorates HFD-mediated hyperlipidemic and diabetic changes. Periodic change in (A) BW; (B) BG levels in WT and PPAR-γ−/− mice fed with chow or HFD. (C) Glucose test tolerance; (D) Insulin test tolerance in WT- HFD and PPAR-γ−/−− HFD mice. (E-F) Cumulative food intake and calorie intake over time among the experimental groups. (G) Storage body fat composition among WT and PPAR-γ−/−. (H-I) Glut4 expression and its quantification from LV heart normalized with GAPDH in WT and PPAR-γ−/− mice fed with chow or HFD. Serum levels of (J) TC; (K) FFA; and (L) TG in WT and PPAR-γ−/− mice fed with chow or HFD. (M-N) Oil-red-O staining of LV heart and its quantification in WT and PPAR-γ−/− mice fed with chow or HFD (*p<0.05 chow vs HFD, #p<0.05 WT-HFD vs PPAR−/−− HFD).
