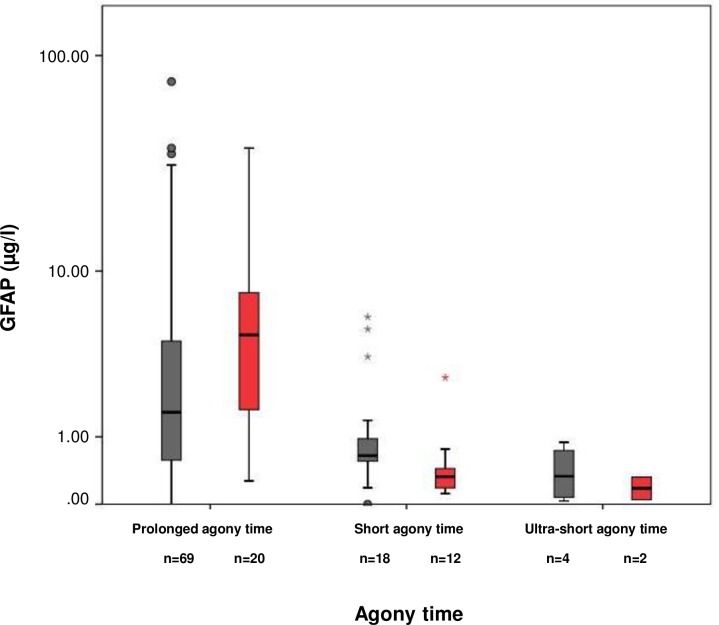
Fig 3. Post-mortem GFAP serum concentrations of the *brain injury group.
Post-mortem GFAP serum concentrations of the *brain injury group (including all cases with a primary cerebral cause of death, all cases having macroscopic changes in brain integrity [such as cerebral edema and cerebral hemorrhage], and all cases in which the brain was exposed to hypoxia or ischemia [i.e., respiratory cause of death, exsanguination, multi-organ-failure, resuscitation]) and the control group (without brain injury) stratified according to agony time. GFAP concentrations of the brain injury group (grey bars): ultra-short agony times (median 0.35μg/l [IQR 0.76, minimum 0.03, maximum 0.83]; n = 4), short agony times (0.64μg/l [0.51, 0.10, 5.87]; n = 18), and prolonged agony times (1.58μg/l [3.91, 0.21, 76.25], n = 69; Kruskal Wallis p = 0,018; post-hoc ultra-short versus prolonged agony times p = 0.032, short versus prolonged agony times p = 0.041) GFAP concentrations of the control group (without brain injury; red bars): ultra-short agony times (median 0.19μg/l [IQR 0.27, minimum 0.05, maximum 0.32]; n = 2, p = 0.643), short agony times (0.33μg/l [0.30, 0.12, 2.68]; n = 12), and prolonged agony times (4.71μg/l [7.33, 0.27, 38.00], n = 20; Kruskal Wallis p<0.001; post-hoc ultra-short versus prolonged agony times p = 0.040, short versus prolonged agony times p<0.001).