Fig. 1. Compartmentalized design of a human motor unit on a chip microfluidic device.
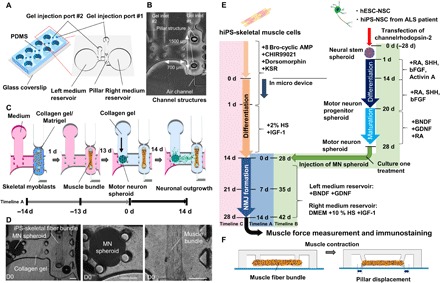
(A) The micro fabricated motor unit mimic device uses polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels to form four identical sites on a single chip, each composed of a muscle fiber bundle attaching pillar structures and culture MN spheroids. Each site has two medium reservoirs, two gel injection ports, and three compartments. (B) Photos of the microfluidic device. Each device had three distinct culture regions: for MN spheroids (left), muscle tissues (right), and neurite elongation (middle). The distance between two pillars is 1500 μm. (C) iPS-derived skeletal myoblasts were injected into the right compartment with the collagen/Matrigel mixture from gel injection port 1. Within 1 day, a skeletal muscle fiber bundle was formed on pillar structures. After 13 days of differentiation, an MN spheroid with collagen gel was injected into the left compartment from gel injection port 2. Neural outgrowth occurs by 14 days, resulting in the formation of a human motor unit along with NMJ. (D) An MN spheroid and a skeletal muscle fiber bundle in a microfluidic chip on day 0 (D0). A differentiated MN spheroid and a muscle fiber bundle were embedded in collagen gel. Scale bars, 200 μm. (E) Preparation and differentiation of skeletal muscle cell and MN cells. hESC-derived NSC spheroids were formed and differentiated into mature MNs by treatment with appropriate growth factors. Meanwhile, hiPS-derived skeletal muscle fiber bundles were formed in the microfluidic device and differentiated into mature myotubes. Then, an MN spheroid was injected for coculture of the two tissues. Timeline A indicates 0 d = initial day of coculture; timeline B indicates 0 d = initial day of generating neurospheorid; and timeline C indicates 0 d = initial day of seeding skeletal muscle cells into the device. KSR, knockout serum replacement; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; SHH, sonic hedgehog; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, glial cell–derived neurotrophic factor. (F) Muscle contraction force driven by electrical stimulation and chemical stimulation via MN is estimated by pillar displacement.
