Fig. 5. ALS patient–derived motor unit and drug treatment.
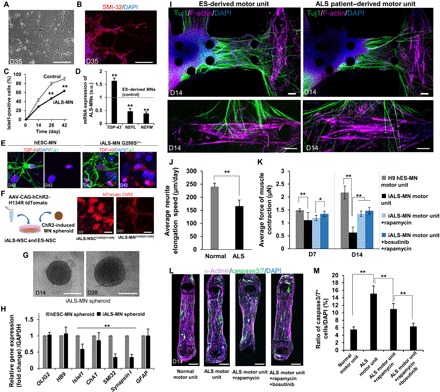
(A and B) Morphology and immunostaining of SMI-32 (red) and DAPI (blue) of ALS patient–derived iPS MNs on D35 after differentiation. The expression of neurofilament heavy chain indicates maturation of MNs. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Percentage of islet1-positive cells of iALS-MN is lower than that of control (ESC-derived MNs) (counting 100 cells, n = 5). (D) TDP-43 expression is higher than that of control, whereas expression of NEFL and NEFM is lower than that of control. n = 3. Scale bars, 20 μm. a.u., arbitrary units. (E) Immunostaining of TDP-43 (red) indicates abnormal aggregation and inclusion in iALS-MN G298S compared with control (hES-MN). (F) Transfection of channelrhodopsin-2[H134R] in ALS patient–derived NSCs. Scale bars, 20 μm. (G) Representative images of iALS-MN spheroids on D14 and D28. Scale bars, 200 μm. (H) Comparison of mRNA expression on D45 related to MN differentiation between iALS-MN spheroids and ESC-derived MN spheroids revealed that no significant changes were observed in OLIG2, HB9, and GFAP. In contrast, the decrease in islet1, ChAT, SMI-32, and Synapsin I indicated an immature function of neural activity. n = 8. (I) Representative images of the ALS motor unit and control D14 of coculture stained by Tuj1 (green), F-actin (purple), and DAPI (blue). Fewer thick neural fibers and less NMJ formation were seen on the ALS motor unit model compared with the ES-derived motor unit. Scale bars, 100 μm. (J) Average neurite elongation speed in the ALS motor unit was slower than that in control. (K) Treatment of potential drugs (bosutinib and rapamycin) to the ALS motor unit model. n = 4. Muscle contraction of the ALS motor unit was weaker than that of the ES-derived motor unit without drug treatment on D7 and D14. No significant effect of the drug treatments on D7. However, significant neuroprotection by treatments can be seen on D14. (L and M) After D14 of culture in the microfluidic system with the MN spheroid, muscle fiber was live stained for caspase3/7 and then stained for α-actinin and DAPI. In the normal motor unit (ESC-derived MN and iPS-derived skeletal muscle), few caspase3/7-positive cells can be observed. The number of caspase3/7-positive cells increased in the ALS motor unit (iALS-MN and iPS-derived skeletal muscle). Treatment with rapamycin and rapamycin/bosutinib significantly decreased the number of caspase3/7-positive cells, indicating that the treatment of drug reversed muscle apoptosis. n = 2. Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Student’s t test and two-way ANOVA. Error bars ± SD.
