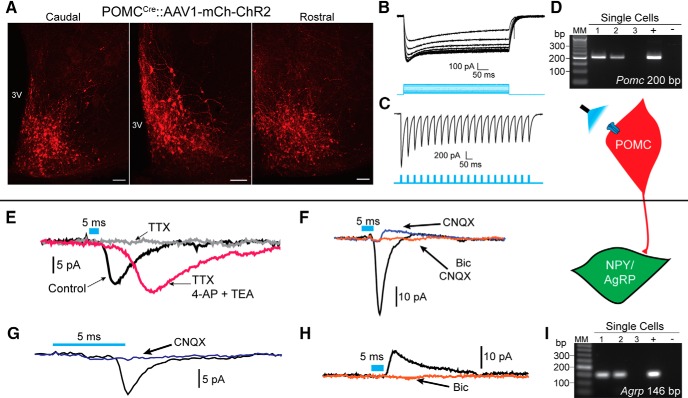
Figure 3.
Optogenetic activation of POMC neurons produces postsynaptic responses in NPY/AgRP neurons. A, Confocal images (10×) of serial 240-μm coronal brain slices from an ARH-injected POMCCre::ChR2:mCherry mouse. B, Optogenetic (470-nm light) stimulation produced strong, sustained inward currents. C, Channelrhodopsin currents in POMC neurons are able to faithfully follow 20-Hz optogenetic stimulation. D, Single cells harvested from fluorescent cells that responded with direct channelrhodopsin currents. E, Postsynaptic nature of responses was confirmed when they were rescued from 1 μM TTX after coapplication of 0.5 mM 4-AP and 7.5 mM TEA. F, Both CNQX-sensitive, inward, and bicuculline-sensitive, outward currents were detected. G, Using a standard K+ gluconate internal solution and holding Vm at -60 mV, glutamatergic currents were primarily encountered. H, Less frequently, GABAergic currents could be observed. Traces are the average of 50 sweeps, blue bars representing optogenetic stimulation are 5 ms for postsynaptic responses. Scale bars: 100 μm. I, Single cells harvested following recordings which displayed a postsynaptic current. The majority could be identified as NPY/AgRP neurons post hoc for inclusion in subsequent analyses.