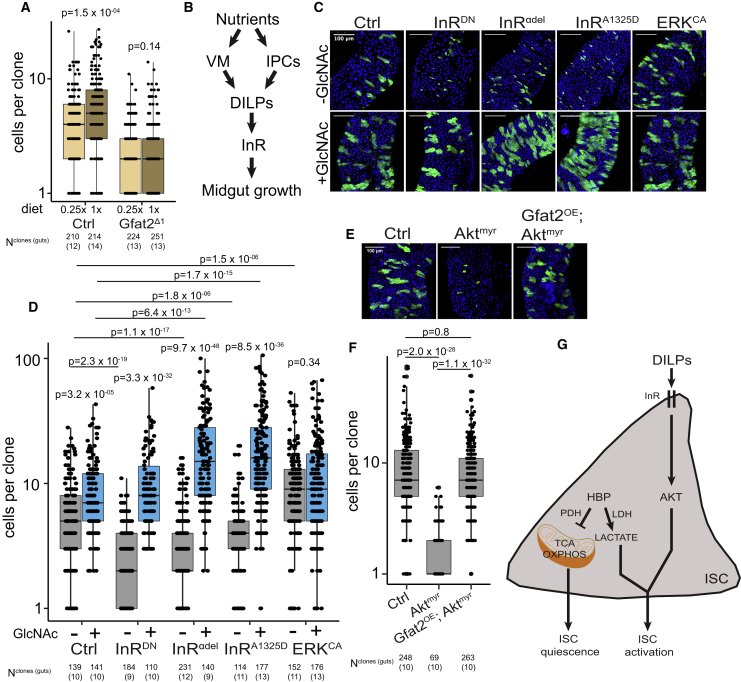
Figure 4.
HBP Is an Essential Facilitator of InR-Mediated ISC Proliferation
(A) Gfat2 is necessary for nutrient-dependent midgut adaptation. Quantification of the cell numbers in control and gfat2Δ1 MARCM clones in the control diet (1×) and calorie-restricted diet (0.25×).
(B) Schematics of the role of nutrients in ISC extrinsic control of midgut growth. Feeding elicits local insulin (DILPs) production from visceral muscle (VM) and brain insulin-producing cells (IPC). Insulin activates the ISC insulin receptor (InR) signaling leading to ISC activation to cell growth and division.
(C) HBP is an essential facilitator of InR signaling-mediated ISC proliferation. MARCM clones of control, InRDN, InRCA (InRαdel & InRA1325D), and ErkCA in the absence or presence of dietary GlcNAc in control 1× diet.
(D) Quantification of (C).
(E) HBP is an essential facilitator of Akt-mediated ISC proliferation. Control, Aktmyr, and Gfat2; Aktmyr expressing MARCM clones in control 1× diet.
(F) Quantification of (E).
(G) A model deciphering the role of HBP in ISC activation. HBP activity regulates the balance between oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis-mediated lactate production and ISC quiescence and activation, respectively. p values in (A), (D), and (F) are calculated by Wilcoxon rank-sum test with multiple testing correction (FDR < 0.05). The number of samples in the clonal experiments are indicated in the figure and in Table S3.
See also Figure S4.