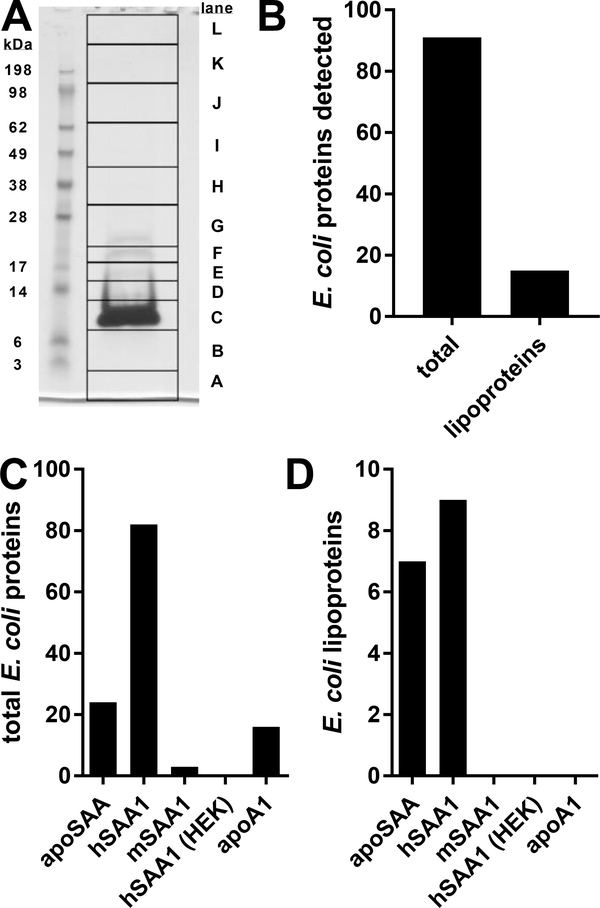
Figure 4.
apoSAA contains bacterial lipoproteins. 50 ¼g of apoSAA was reduced, denatured, and separated by PAGE (A). The 12 indicated regions were subjected to in-gel digestion with trypsin. The extracted tryptic peptides were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and the resulting spectra were searched against a database for human and E. coli proteins, including predicted and probable E. coli liproteins (B). Six ¼g of SAA from different sources were digested in-solution and similarly analyzed by mass spectrometry. Total E. coli proteins identified (C) as well as predicted and probable E. coli lipoproteins identified (D) are indicated. Data are from two independent experiments.