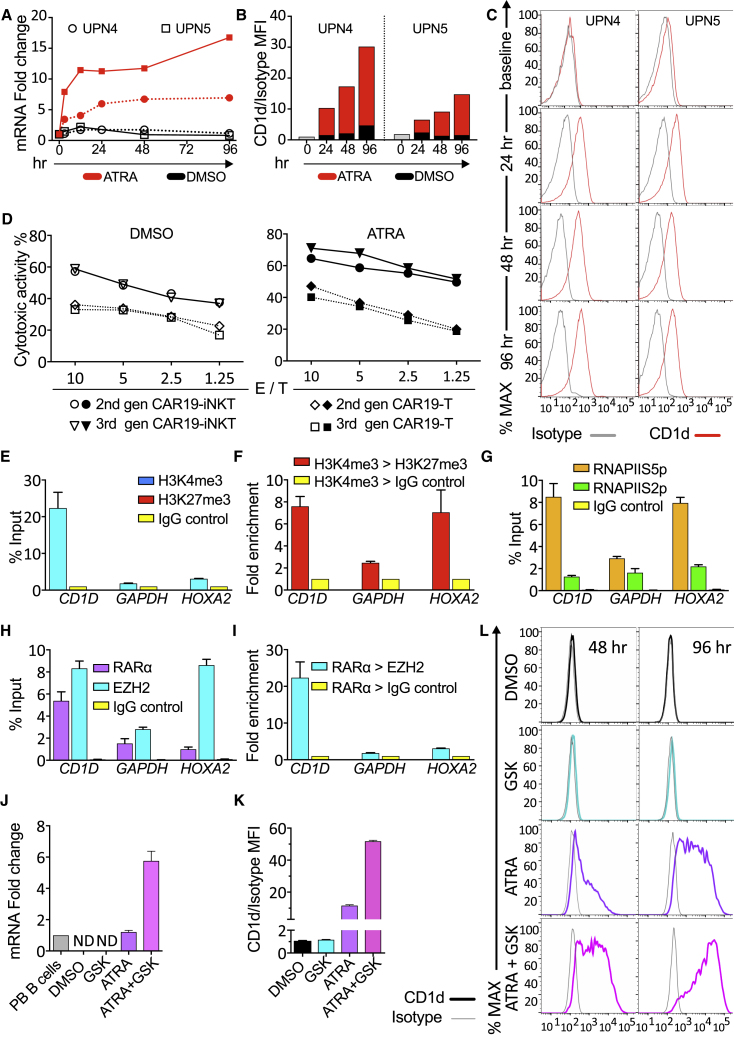
Figure 4.
Transcriptional and Epigenetic Basis for Enhancing CAR19-iNKT Cell Reactivity
(A) CD1D mRNA quantification by qPCR in CLL cells from two patients upon ATRA treatment (10−6 M) for 0–96 hr.
(B and C) Bar charts (B) and flow cytometry histograms (C) showing CD1d expression on malignant B cells upon ATRA treatment and mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) analysis of CD1d expression in comparison with isotype control.
(D) Cytotoxicity of second- and third-generation CAR19-T and -NKT cells against αGalCer-pulsed CLL cells pre-treated with 0.1% DMSO control or 10−6 M ATRA. Error bars represent SEM of triplicate assays.
(E) ChIP-qPCR assay for H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 enrichment in the promoter of CD1D using IgG as control in U266 cells. GAPDH is an active gene control, while HOXA2 is a repressed gene control. ChIP data are shown as a percentage of the input chromatin.
(F) ChIP-re-ChIP qPCR assay showing fold enrichment of H3K27me3 or IgG control after immunoprecipitation (IP) against H3K4me3.
(G) ChIP-qPCR assay against RNA Pol II for Ser5 over Ser2 phosphorylated form at the promoter of the indicated genes.
(H) ChIP-qPCR assay against RARα, EZH2, and Ig control at the promoters of the genes shown.
(I) ChIP-re-ChIP qPCR assay showing enrichment of EZH2 or IgG control after IP against RARα in U266 cells for –(I) (n = 3).
(J) qPCR quantification of CD1D mRNA in U266 cells treated with 0.1% DMSO, 10−6 M GSK343, 10−6 M ATRA or 10−6 M GSK343 plus 10−6 M ATRA. Values are normalized to CD1D mRNA expression levels in normal peripheral PB B cells (n = 3). ND, not detectable.
(K and L) Relative MFI analysis (K) and histogram depiction (L) of CD1d expression in comparison with isotype control in U266 cells from the same experiment shown in (J).
Error bars represent SEM. See also Figure S4.