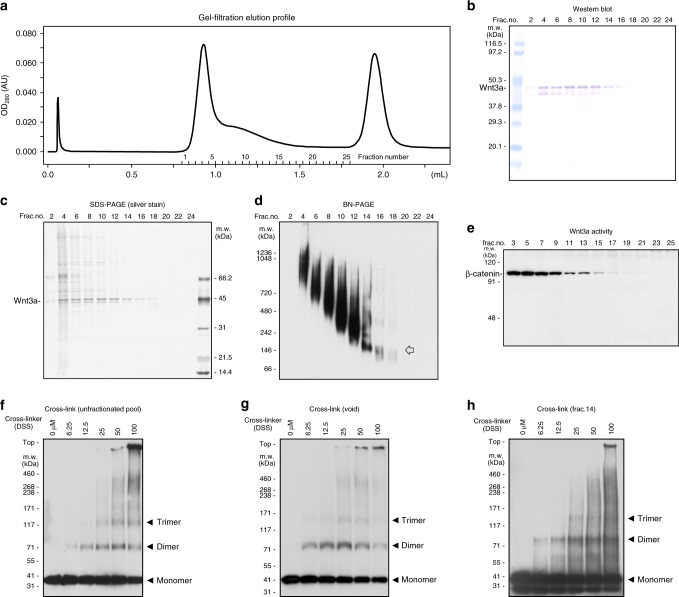
Fig. 3.
Characterization of Wnt3a fractionated by gel filtration. a Elution profile of gel filtration column chromatography. Affinity-purified FLAG-Wnt3a proteins, prepared from serum-free medium conditioned with FLAG-Wnt3a-secreting L cells, were subjected to gel filtration column chromatography (Superdex200 PC3.2/30, GE Healthcare). b Analysis of fractionated proteins by western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody. Wnt3a proteins are recovered in widely spread fractions, including a fraction corresponded to the void volume (fraction #4). c Analysis of fractionated proteins by silver staining. Protein whose size corresponded to FLAG-Wnt3a is the major component in fractions from fraction #2 to #16. d Analysis of fractionated proteins by western blotting using Blue Native PAGE (Invitrogen), which can separate high-molecular-weight proteins while maintaining their native conformation. This analysis shows that the size of Wnt-3a protein complex is mostly distributed between ~150 kDa and 1000 kDa. Of note, a discrete band corresponding to 150 kDa is detected in fraction 14. An arrow indicates a discrete band whose molecular weight corresponded to the size of a Wnt trimer. e Wnt signaling activity assessed by application of each fraction to mouse L cells. Since the β-catenin protein level is quite low in the absence of Wnt signaling in L cells, we directly monitored Wnt signaling activity by measuring the β-catenin protein level in these L cells. All of the fractions in which FLAG-Wnt3a was detectable increased the β-catenin level, indicating that Wnt3a protein still possessed its signaling activity. f–h Cross-linking analysis with proteins in unfractionated pool (f), in void volume (g), and in fraction 14 (h). Full blot images of b–h are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9