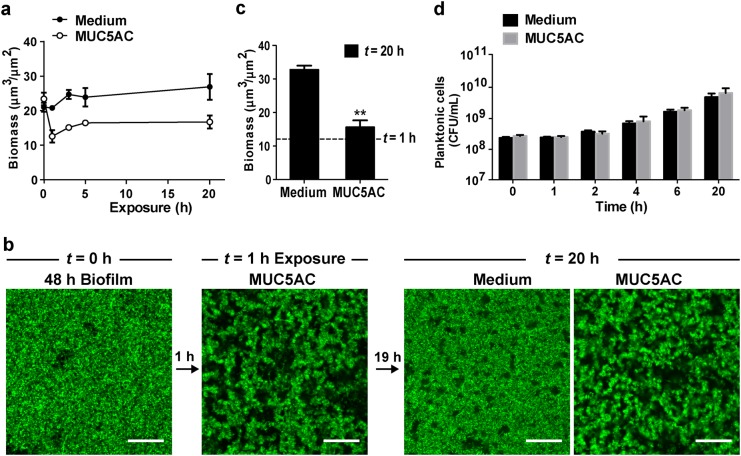
Fig. 2.
Mucins disrupt P. aeruginosa biofilms without killing the bacteria. a Prolonged mucin exposure suppresses biofilm development. 48 h PAO1-GFP biofilms were exposed to medium with or without MUC5AC (0.5% w/v) over 20 h and the remaining surface-attached biofilm biomass quantified. Error bars represent standard error (n = 3). b Biofilms eroded by exposure to mucins remain viable. 48 h PAO1-GFP biofilms were first eroded via exposure to 0.5% MUC5AC for 1 h at 0.5 μL/min flow, then incubated for an additional 19 h in medium containing MUC5AC as indicated. Biofilms resumed development after being moved to mucin-free medium, indicating that eroded biofilms are still viable. Scale bars = 20 μm. c Quantification of biofilm biomass at 20 h. Dotted lines indicate value after the initial 1 h mucin treatment. Error bars represent standard error (n ≥ 3). **P ≤ 0.005, unpaired Student’s t test. d Exposure to mucins does not significantly impair P. aeruginosa viability. PAO1-GFP cells were grown in suspension in medium with or without 0.5% mucins. Colony-forming units (CFUs) were counted to assess cell viability. Error bars represent standard error (n = 3)