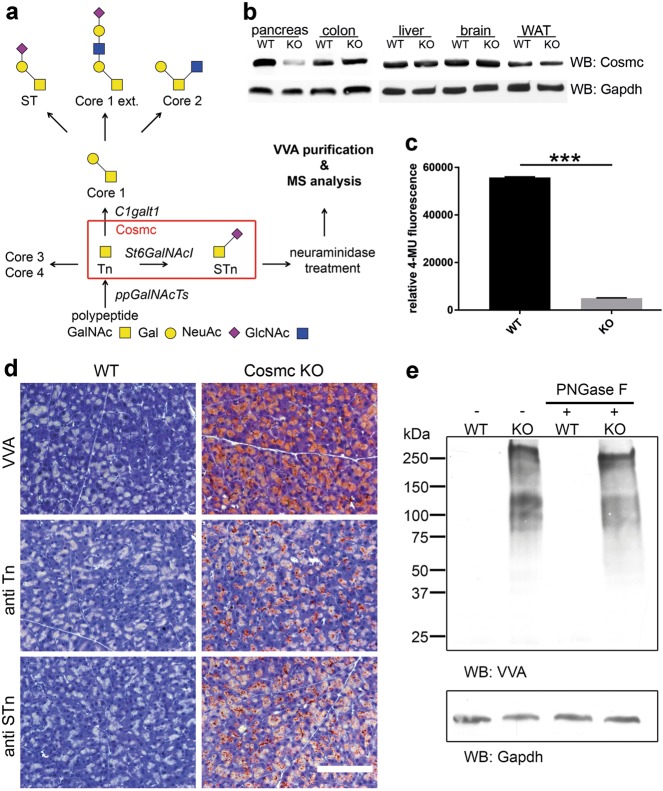
Fig. 1. Deletion of Cosmc results in loss of core 1 glycan formation.
a Scheme of O-glycosylation pinpointing the role of Cosmc. Depending on the biological context, a set of expressed ppGalNAcTs transfer GalNAc moieties to serine and threonine residues of the target proteins. Subsequent extension from Tn antigen to core 1 is performed by C1galt1 (T-synthase) being folded and stabilized by Cosmc. Lack of T-synthase activity results in Tn and STn expression. b Anti-Cosmc Western blot analysis of pancreas, colon, liver, brain and white adipose tissue (WAT) lysates derived from WT and pancreas-specific Cosmc-KO mice. Clearly reduced Cosmc protein is observed in KO pancreatic tissue. c The fluorescent T-synthase assay further validated reduced T-synthase activity in Cosmc-KO pancreatic tissue compared to WT (n = 4). d Representative histochemical staining using VVA on FFPE WT and Cosmc-deficient mouse pancreata demonstrates specific binding to acinar cells in Cosmc KO. Further, antibodies directed against Tn and STn antigens specifically detected pancreatic acinar cells in Cosmc KO. The scale bar equals 50 µm. e Far-Western blot analysis of whole-pancreatic tissue lysates of Cosmc-KO mice display Tn antigen expression on a variety of proteins, whereas no reactivity is observed in lysates of WT littermates. PNGase F treatment did not alter VVA reactivity in Cosmc-KO lysates, emphasizing VVA specificity towards O-linked GalNAc