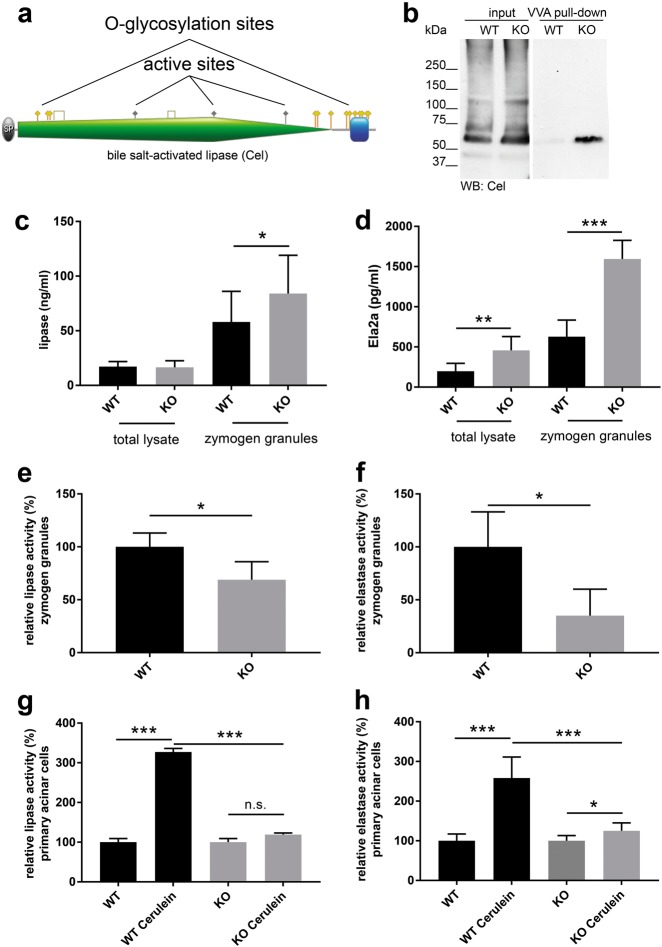
Fig. 2. Cosmc-dependent O-GalNAc glycosylation affects pancreatic lipase and elastase enzyme function as well as exocrine pancreas secretion.
a Scheme of bile salt-activated lipase (Cel) protein domains (SP, signal peptide; carboxylesterase, type B, green; PEST domain, blue; O-GalNAc glycosylation sites, yellow; active sites, gray). b Representative WB of VVA pull-down from WT and Cosmc-KO pancreatic lysates and Cel-specific antibody for detection. Note: Distinct Cel protein bands were robustly detected in pull-downs from KO tissue. c Absolute quantification of lipase in total lysates and zymogen granule lysates from WT and Cosmc-KO mice (n = 18). Total lysates display equal amounts of lipase (P = 0.748), whereas elevated levels are detected in Cosmc-KO zymogen granules (P = 0.023). d Absolute quantification of elastase (Ela2a) in total and zymogen granule lysates from WT and Cosmc-KO mice (n = 18). Lysates derived from Cosmc KO display significantly elevated elastase. (e + f) Relative lipase and elastase activities in zymogen granule lysates from WT and Cosmc-KO mice (n = 4) using 4-MU substrates reveal decreased activities in KO. (g + h) Analysis of lipase and elastase activities in response to cerulein stimulation of WT and Cosmc-KO primary pancreatic acinar cells. Cerulein-induced lipase and elastase secretion is detectable in WT cells (P = 0.0001) and is attenuated in Cosmc-KO mice (P = 0.611 and P = 0.04). Relative difference in stimulated lipase activity is P = 0.0001