Fig. 3.
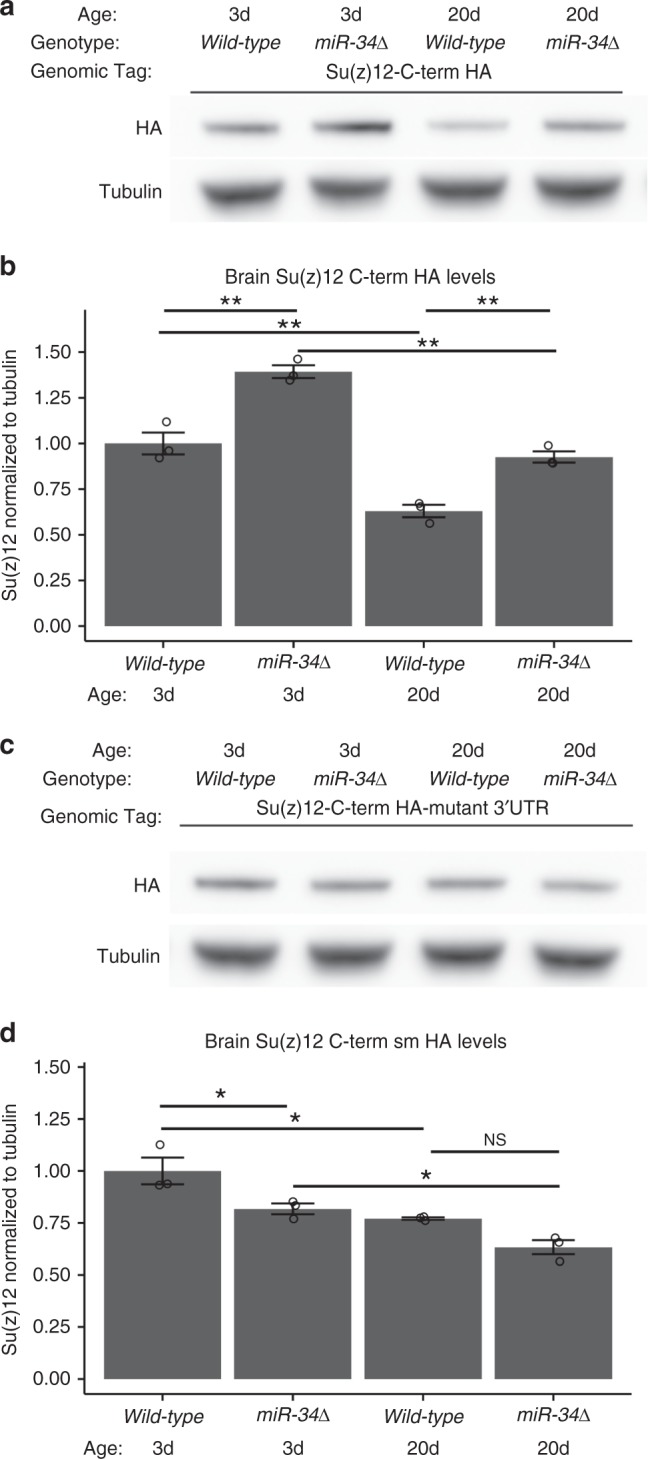
Su(z)12 is a target of miR-34 in the brain. a, b Su(z)12 protein levels are deregulated in miR-34 mutants. Su(z)12 protein was detected using a transgene containing the Su(z)12 genomic region tagged with the HA epitope on the C-terminus of the predicted protein (Su(z)12-C-term HA). Su(z)12 levels decreased with age in wild-type, but remained elevated in miR-34 mutants. Protein samples from dissected brains. Su(z)12-C-term HA protein levels were normalized to tubulin loading control. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biological replicates. Significant main effects were observed (genotype: F1,8 = 68, p < 0.001 age: F1,8 = 101, p < 0.001). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test).c, d The regulation of Su(z)12 protein levels by miR-34 is dependent upon the miR-34 seed sequence in the 3′UTR of the Su(z)12 transcript. The Su(z)12-C-term HA-mutant 3′UTR transgene contains a mutation in the miR-34 seed sequence that relieves the transcript from regulation by miR-34 (see Fig. 1d). Su(z)12-C-term HA-mutant 3′UTR protein levels still decrease with age, but are no longer increased in miR-34 mutants. The difference between wild-type at 20d and miR-34 mutant at 20d is not significant. Protein samples from dissected brains. Quantification of Su(z)12-C-term HA-mutant 3′UTR protein levels using Western immunoblotting, normalized to tubulin loading control. Mean ± SEM, n = 3 biological replicates. Significant main effects were observed (genotype: F1,8 = 17, p < 0.01 age: F1,8 = 28.5, p < 0.001). (*p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test)
