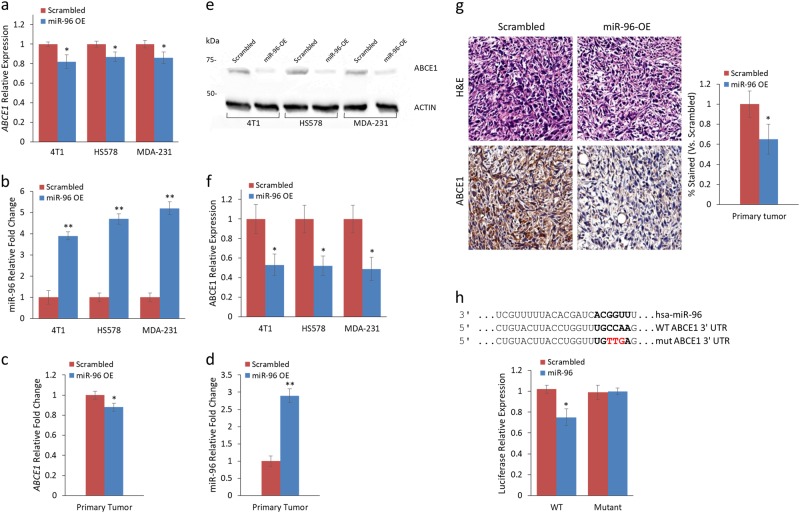
Fig. 2. ABCE1 gene and protein expression are reduced in direct response to miR-96 overexpression in vitro and in vivo.
a ABCE1 and b miR-96 expression levels in 4T1, HS578, and MDA-231 cell lines expressing miR-96 OE or scrambled control. ABCE1 expression is reduced in all cell lines with miR-96 OE. c ABCE1 and d miR-96 expression in primary tumors of mice injected with miR-96 overexpressing or scrambled control 4T1 cells. ABCE1 and miR-96 expression levels are inversely correlated. e Western blot of ABCE1 in breast cancer cell lines and f calculated ABCE1 protein expression in cell lines with miR-96 OE or scrambled control. ABCE1 expression is twofold decreased in miR-96 OE cells compared to scrambled control. g H&E and immunohistochemistry for Abce1 of resected murine primary breast tumors. Reduced Abce1 staining is seen in miR-96 OE compared to Scrambled. h Predicted binding site (indicated by bold letters) for hsa-miR-96 on the ABCE1 3′-UTR and Luciferase activity 24 h following co-transfection of HeLa cells with hsa-miR-96 and ABCE1 WT or Mut 3′-UTR construct. Wild type (WT) and mutant (Mut) miR-96 binding sites are presented. Red nucleotides represent the three mutated nucleotides in the miR-96 seed binding site. Data are presented as mean+/− SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01