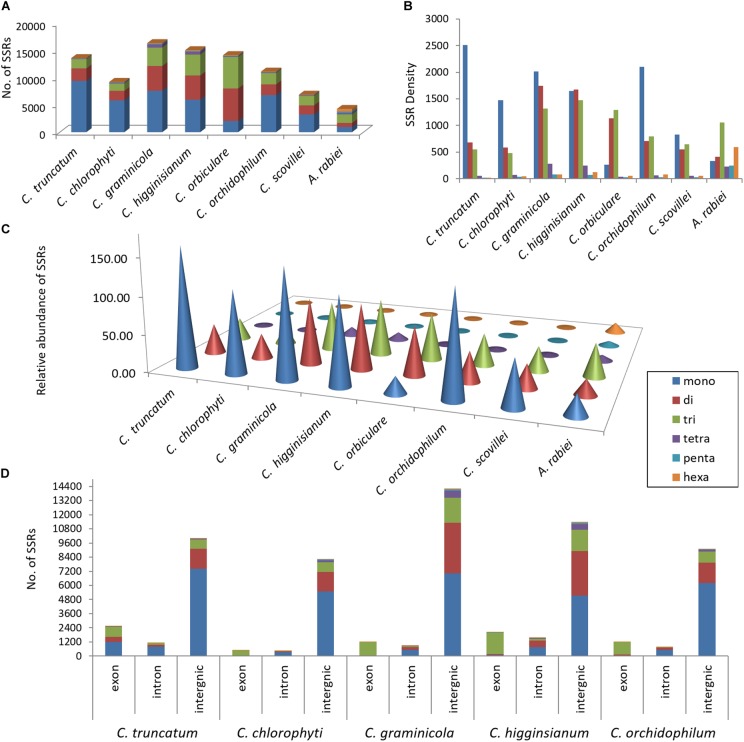
FIGURE 5.
Composition of SSRs in seven Colletotrichum species showing the distribution of SSRs in genomes in terms of (A) their number, (B) relative density (size of each SSR type in bp/Mb of genome), (C) relative abundance (number of SSRs/Mb of genome), and (D) the number of SSRs in coding (exons) and non-coding regions (introns, intergenic regions). Ascochyta rabiei was taken as a reference for accuracy of SSR detection. In all the species, the mononucleotide repeats were the most abundant SSR type except for C. orbiculare, in which tri- and di-nucleotide repeats were more predominant. SSRs were mainly concentrated in intergenic regions. Exons had high proportion of trinucleotide repeats in four species, whereas mononucleotide repeats were more than the trinucleotide repeats in coding region of C. truncatum.