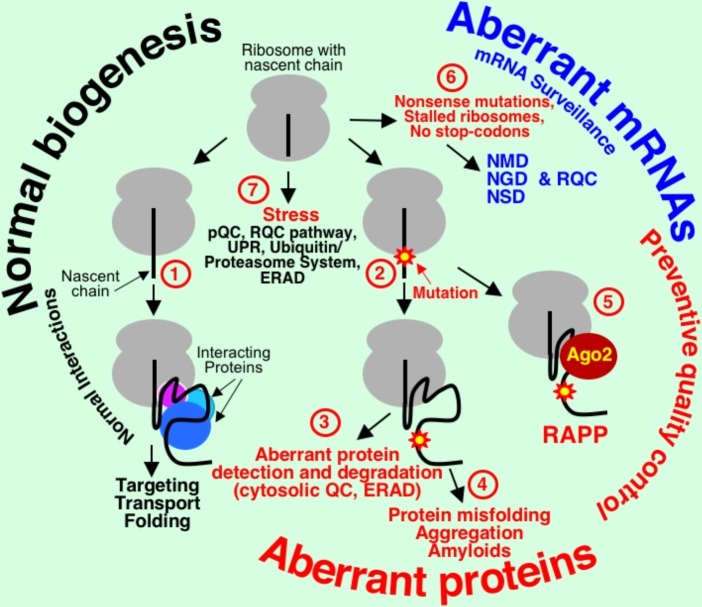
FIGURE 1.
mRNA and protein quality control pathways in mammalian cells. Normal interactions of the nascent chains lead to proper protein transport/folding (1). Loss of these interactions due to defect in the interacting factor or mutation in the polypeptide nascent chain (2) leads to protein degradation (3), misfolding, aggregation, and amyloid formation (4), or mRNA elimination in the RAPP pathway (5). mRNA surveillance quality control systems (6), nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), non-stop decay (NSD), and no-go decay (NGD) detect and eliminate defective mRNAs with PTCs, mRNAs without natural stop codon, and mRNAs at the stalled in translation ribosomes, respectively. Nascent chains at the stalled ribosomes or during stress are ubiquitinated in the ribosome quality control complex (RQC) pathway and removed by proteasome. During ER stress pre-emptive quality control (pQC) cotranslationally reroutes secretory and membrane proteins to cytoplasm for degradation. Many proteins are misfolded during stress and they are removed by multiple cellular systems, like UPR, ERAD, and ubiquitin/proteasome system (7).