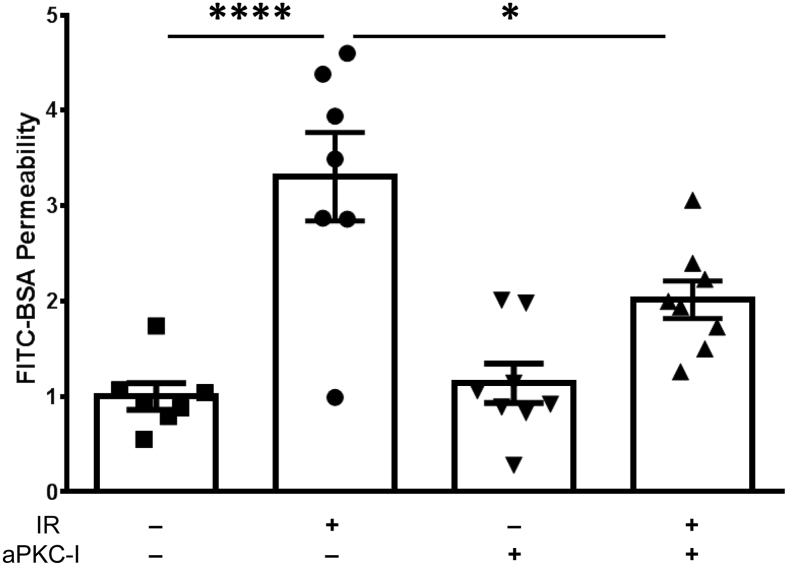
Figure 5.
aPKC inhibitor blocks ischemia-reperfusion (IR)–induced permeability. Rats were injected intravitreally with vehicle [0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in phosphate-buffered saline] or 1 μmol/L of aPKC inhibitor (aPKC-I) at 30 minutes before IR injury. At 24 hours after IR, animals received another intravitreal injection of vehicle or aPKC-I. Fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated (FITC) BSA (100 mg/kg body weight) was injected 30 minutes later and allowed to circulate for 2 hours, and the retinal dye accumulation was determined as a measure of vascular permeability. Results are expressed relative to the vehicle-sham. Statistical analysis was performed using analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc test. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.