-
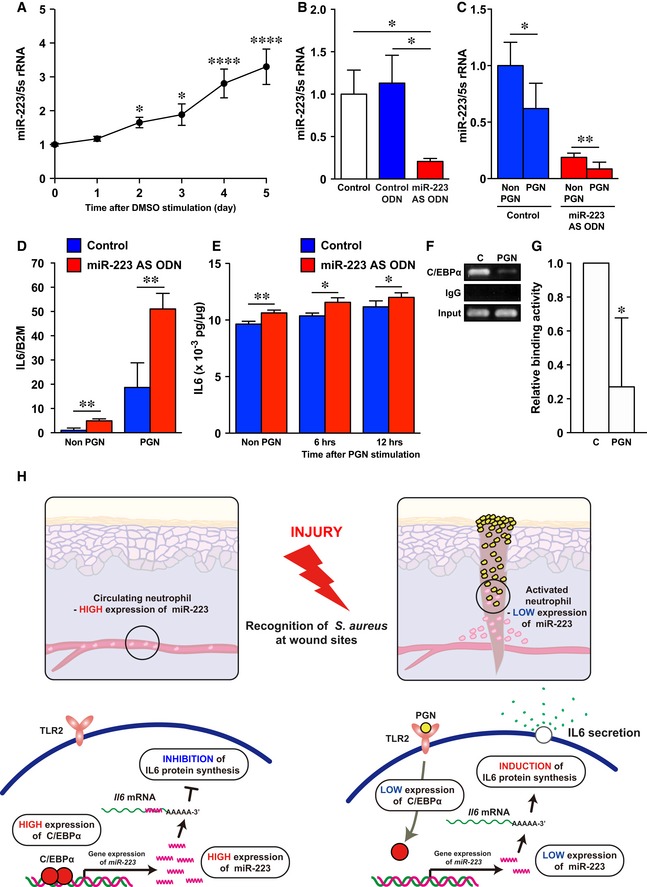
A
qPCR analysis was used to determine the expression levels of miR‐223 in dHL‐60 (n = 3).
-
B
miR‐223 AS ODN decreased miR‐223 expression in dHL60 (control; n = 5, control ODN and miR‐223 AS ODN; n = 6).
-
C
Downregulation of miR‐223 expression in dHL60 cells at 6 h after stimulation with PGN (n = 6).
-
D
qPCR analysis indicates the expression levels of Il6 relative to beta‐2‐microglobulin (B2m) in non‐stimulated and PGN‐stimulated (6 h) dHL60 cells were markedly increased compared with controls (n = 3) after miR‐223 knockdown.
-
E
ELISA revealed non‐stimulated and PGN‐stimulated dHL60 cells constitutively secreted IL‐6 (n = 3–6).
-
F
Decreased C/EBPα binding activity to the
miR‐223 promotor after PGN stimulation (PGN) in dHL‐60 cells compared with non‐stimulated dHL‐60 cells (C, control) revealed by ChIP assay. Full scans for electropherogram in Fig
EV5C.
-
G
Quantification of anti‐C/EBPα Ab‐ChIP relative to non‐stimulated dHL‐60 cells using ChIP‐qPCR (n = 3).
-
H
A model summarizing the interplay between S. aureus, C/EBPα, miR‐223, and IL‐6 secretion in neutrophils at wound sites.
Data information: All values represent the mean ± SD. Ordinary one‐way ANOVA followed by Holm‐Sidak multiple comparisons test was used to generate
P‐values (day 0 versus each day) (A). Unpaired
t‐tests (C–E, and G) followed by Welch's correction (B) were used to generate the
P‐values indicated. *
P < 0.05, **
P < 0.01, ****
P < 0.0001.
Source data are available online for this figure.