FIGURE 3:
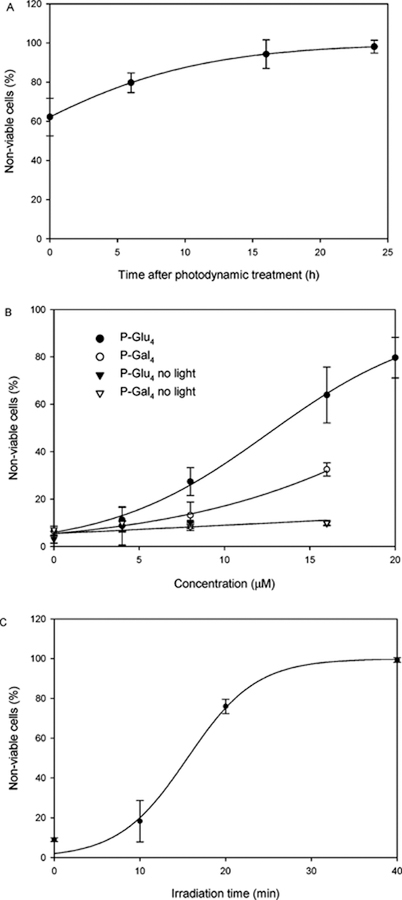
Photocytotoxic effects on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Nonviable cells were counted with hemacytometer after staining with 0.4% w/v trypan blue. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 20 µM P-Glu4 for 24 h, rinsed by exchanging the growth medium, and irradiated under a white 13 W fluorescent light (0.94 mW cm−2 for 20 min; 11.28 kJ m−2). The nonviable cells were counted at various lengths of time after photodynamic treatment. (B) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with various concentrations of P-Glu4 (•) or P-Gal4 (ï) for 24 h, rinsed by exchanging the growth medium, and irradiated under a white 13 W fluorescent light (0.94 mW cm−2 for 20 min; 11.28 kJ m−2). Six hours after photodyamic treatment, nonviable cells were counted. Control experiments with no light show that MDA-MB-231 cells remain viable in the presence of the porphyrin-saccharide conjugates (▼, ▼). (C) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 20 µM P-Glu4 for 24 h, rinsed by exchanging the growth medium, and irradiated under a white 13 W fluorescent light (0.94 mW cm−2) for various lengths of time. Six hours after photodynamic treatment, nonviable cells were counted. Each data point represents an average ± SD from at least three independent measurements.
