Fig. 2.
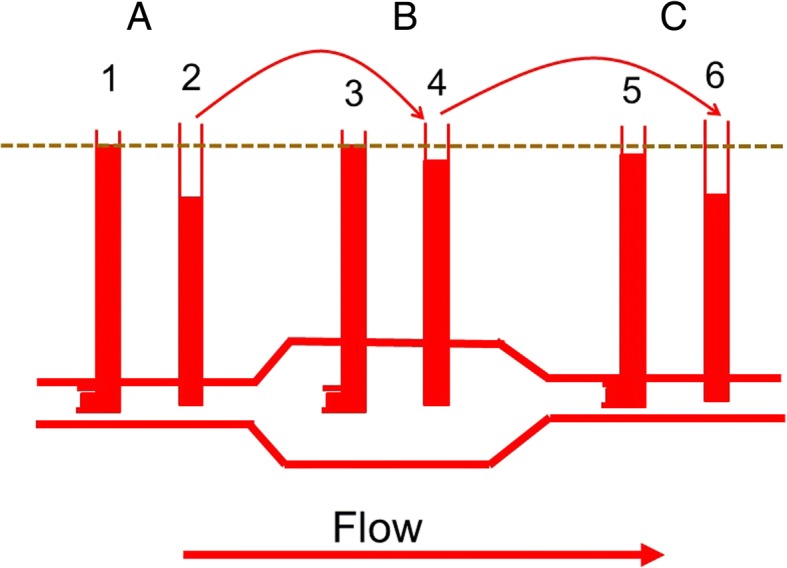
Pressure measurements in a vessel with an aneurysmal region. Pressures measured with fluid filled tubes facing the flow [1, 3, 5] measure elastic and kinetic energy, whereas tubes with the opening perpendicular to the flow just measure lateral pressure [2, 4, 6]. An assumption is that the energy loss due to resistance (dashed line) is minimal. In A, the tube facing the flow [1] shows a higher pressure than the tube measuring lateral pressure [2] because it includes kinetic energy. In B the vessel diameter is larger and velocity of flow is slower. The kinetic energy converts into elastic energy and the difference between tubes 3 and 4 is much smaller than between 1 and 2. In C, the tube narrows again so that kinetic energy increases and lateral energy decreases, which again increases the difference between 5 and 6
