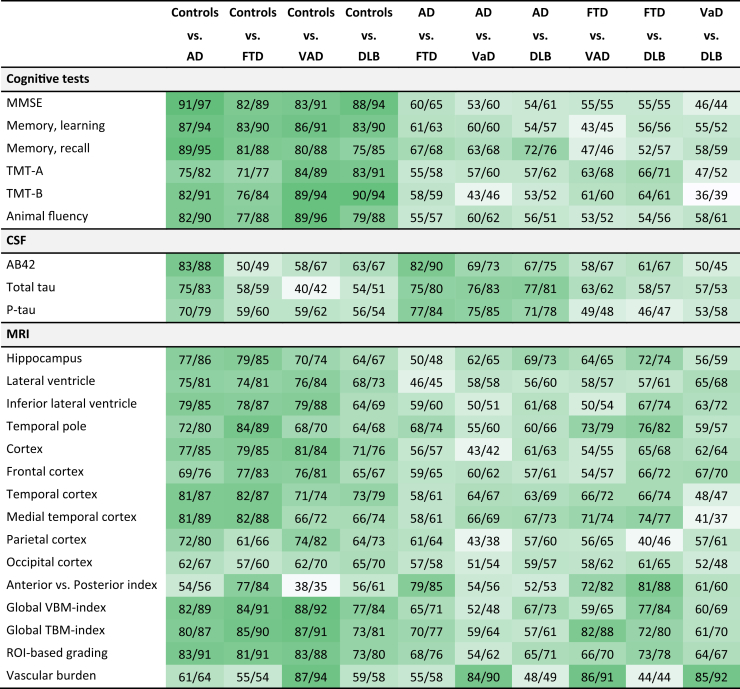
Table 2.
Pairwise comparison of diagnostic groups for all diagnostic tests, reporting balanced accuracy and area under the ROC curve (Bal. Acc./AUC)
Abbreviations: ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AD, Alzheimer's disease; FTD, frontotemporal dementia; VaD, vascular dementia; DLB, dementia with Lewy bodies; MMSE, Mini–Mental State Examination; TMT, Trail Making Test; Aβ42, β amyloid 1–42; p-tau, tau phosphorylated at threonine 181; VBM, voxel-based morphometry; TBM, tensor-based morphometry; ROI, Region of interest; WMH, white matter hyperintensity; AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; Bal.Acc., balanced accuracy; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; RAVLT, Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Task; CERAD, Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease.
NOTE. For each pairwise comparison of two diagnostic groups, a balanced accuracy and AUC (Bal.Acc./AUC) are presented for each diagnostic test. Balanced accuracies 85%–100% are highlighted in dark green. The gradually lighter shades of green indicate lower balanced accuracy with white being at or below 50. Both balanced accuracy and AUC are reported as percentage values (%).
NOTE. Memory: RAVLT values, using z-scoring for those with only CERAD. MRI: volumes are defined from image segmentations produced by a multi-atlas segmentation algorithm. Anterior versus posterior index: index between anterior and posterior weighted volumes. ROI-based grading: based on hippocampus region of interest. The classification for “grading” consists of eight grading features and “vascular burden” consists of three features: volume of WMHs, volume of cortical infarcts, and volume of lacunar infarcts.