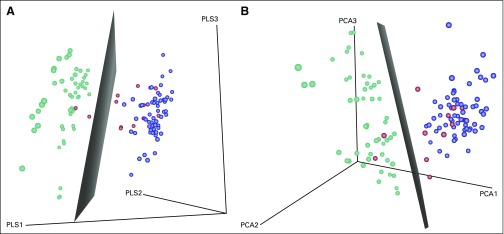
Fig 3.
Analysis of gene expression profiles (GEPs). (A) Principal components analysis of GEPs from immunoglobulin M (IgM) multiple myeloma (MM; red), non-IgM MM (blue), and patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM; green). (B) Partial least squares analysis of GEPs from IgM MM, non-IgM MM, and WM patients. Both methods were used to reduce the dimensionality of the top 1,000 probesets in WM and non-IgM MM groups to three dimensions. The same transformation was applied to IgM MM samples. Then, a linear support vector machine model was applied to the WM non-IgM MM groups, and the boundary plane was plotted. This method reflects the same results as the hierarchical clustering analysis (Fig 2), in that the majority of the IgM MM samples (red) are on the non-IgM MM side of the boundary, indicating that the GEP of IGM MM is more closely related to non-IgM MM subtypes than it is to WM.